DESIGN A SCALABLE BUSINESS MODEL
RESUMEN
Diseñar un modelo de negocio escalable es crucial para el crecimiento sostenido de una empresa. La escalabilidad se refiere a la capacidad de una empresa para aumentar sus ingresos sin un incremento proporcional en sus costos, permitiendo así un crecimiento eficiente y la generación de mayores beneficios. Este aspecto es especialmente relevante para startups y empresas emergentes que buscan crecer rápidamente y atraer inversión.
Claves para la Escalabilidad en Modelos de Negocio:
- Innovación y Tecnología
- Mercado Potencial Grande
- Producto o Servicio Diferenciado
- Eficiencia Operativa
- Modelo de Ingresos Adaptable
- Equipo Capacitado y Motivado
Beneficios de la Escalabilidad:
- Mayor Rentabilidad
- Atractivo para Inversores
- Flexibilidad y Adaptabilidad
Estrategias para Escalar Negocios en Diversos Sectores:
- Digitalización y Automatización
- Capacitación y Expansión de la Red de Colaboradores
- Diversificación de la Oferta
- Uso de Plataformas en Línea para Ventas y Marketing
Crear un modelo de negocio escalable no solo implica el uso inteligente de la tecnología y la innovación, sino también una planificación estratégica que considere el mercado potencial, la diferenciación del producto o servicio, y la eficiencia operativa. La escalabilidad es un factor clave para el éxito a largo plazo de una empresa, permitiendo crecer de manera sostenida y rentable.
Tabla de contenidos
Scalability refers to the a company's ability to grow and increase its revenues without a commensurate increase in its costs. In other words, it is the ability of a company to increase its profitability as its size increases. Scalability is especially important for start-ups, as they need to grow quickly to be successful.
If a company is not scalable, its growth will be limited and it may be difficult for it to succeed. Companies that are scalable often have innovative business models that allow them to grow rapidly. These models may include automation, the use of advanced technology and the outsourcing of certain functions. In summary, scalability is essential to the long-term success of a start-up and can be an important factor for investors when considering investing in a company.
Why is scalability important?
Scalability is important for a business because it allows it to grow and increase its revenue-generating capacity in an efficient and profitable way, without proportionally increasing the costs and resources required. This means that a scalable business can increase its sales and profits without having to increase its infrastructure, staff and expenses in the same proportion.
In addition, Scalability is important because it allows the company to address new markets and growth opportunities, which can help diversify its revenue streams and reduce its dependence on a specific market or product. It can also make the company more attractive to investors and increase its market valuation.
What does it mean for a business model to be scalable?
A scalable business model is one that has the ability to grow and expand without significantly increasing its fixed costs, i.e. the increase in demand does not generate a proportionally high increase in costs. This allows the company to grow and increase its profits more efficiently and sustainably over time.
Why is scalability also good for the entrepreneur, the founder of the company?
Scalability is also good for the entrepreneur for several reasons. Firstly, it allows the company to grow and increase its profits without having to increase its costs proportionally, which translates into higher profitability.
In addition, A scalable business is more attractive to investors, which can make it easier to raise finance and grow the business. Finally, a scalable business can have a more significant impact on its market or on society at large, which can be a motivating factor for the entrepreneur.
Why do business angels only invest in scalable companies?
Business angels generally seek to invest in scalable businesses because they want to maximise the potential return on their investment. Scalable businesses have the ability to grow quickly and profitably, which increases the likelihood of significant returns in the short term. In addition, a scalable business has the ability to continue to generate revenue even after a solid customer base has been reached and breakeven has been exceeded, meaning that it has a greater potential to generate long-term returns.
How do you create a scalable business?
To create a scalable enterprise, it is necessary to design a business model that allows for exponential growth and expansion into new markets without significantly increasing costs.
Below are some steps that can help in this process:
- Identify a large and growing market: It is important that the company has a large enough potential market to be able to grow and expand.
- Develop an innovative and differentiated product or service: the company must offer something unique and attractive to customers, which solves a problem or need efficiently and effectively.
- Implement an effective marketing strategy: the company must be able to reach its target market efficiently and effectively, and to build a strong and recognised brand.
- Automate processes and use technology: the company must leverage technology and automation to increase efficiency and reduce costs.
- Design a scalable business model: the business model must allow for exponential growth without significantly increasing costs.
- To have a skilled and motivated team: it is essential to have a skilled and motivated team that is committed to the company's vision and objectives.
- Obtain adequate funding: the enterprise must have sufficient financing to be able to invest in its growth and expansion.
In a nutshell, creating a scalable business requires a clear vision and an effective strategy that allows for exponential growth without significantly increasing costs, and a team that is skilled, motivated and committed to the vision and goals of the business.
How can I identify the parts of my business model that can be made scalable?
To identify the parts of your business model that can be made scalable, you can follow the steps below:
- Analyse your current business model: start by analysing your current business model and identify the parts that are generating revenue and those that are not.
- Identifies repetitive processes: identifies the repetitive processes in your company that are carried out on a constant basis, either for the production of a product or the provision of a service.
- Assesses growth potential: Assess the growth potential of each of the repetitive processes you have identified. Ask yourself how much growth you could have if you automate or scale up that process.
- Identify the technologies or tools needed: identifies the technologies or tools needed to automate or scale up these repetitive processes.
- Create a plan of action: create an action plan to implement those technologies or tools and scale up your repetitive processes.
- Test and measure the results: Once you have implemented the technologies or tools, test and measure the results to determine if it has been effective in scaling your business model.
Remember that scalability is not just about implementing technology, it may also be necessary to adjust your business model or marketing strategy to reach more customers.
Examples of scalable enterprises:
- Airbnb: this online accommodation platform allows anyone to rent their house, flat or room through the platform, which has allowed it to expand worldwide.
- Uber: this online transport service has revolutionised the way people move around cities, and its scalable business model has allowed it to rapidly expand globally.
- Amazon: the world's largest e-commerce company has a scalable business model that has allowed it to expand into multiple markets and become one of the world's most valuable companies.
- Spotify: this online music platform has changed the way people listen to music and its scalable business model has allowed it to expand to multiple countries around the world.
- Dropbox: This online storage platform allows users to easily save and share files, which has enabled its rapid expansion and growth globally.
- Netflix: this movie and series streaming service has transformed the way people consume audiovisual content, and its scalable business model has allowed it to expand into multiple markets around the world.
- Facebook: the world's largest social network has a scalable business model that has allowed it to expand into multiple markets and become one of the world's most valuable companies.
Scalability in internationalising companies
Scalability is a desirable characteristic for any company, as it allows for rapid and sustainable growth, and this also applies to companies seeking to internationalise. By having a scalable business model, the company can expand into new markets and make the most of growth opportunities.
Some ways to make a company seeking to internationalise scalable are:
- Digitisation: digitisation of business processes and operations can enable faster and more efficient expansion through task automation and improved data management. For example, an e-commerce company can scale its business model internationally through technology.
- Outsourcing: outsourcing certain areas or processes of the company, such as logistics or customer service, can allow for greater flexibility and responsiveness as the company expands into new markets. For example, a company that outsources its logistics can reach new markets more easily.
- Strategic alliances: Strategic alliances can allow the company to take advantage of the experience and knowledge of other companies in the international market and enable faster and more successful entry into new markets. For example, a software company that forms an alliance with a local company can expand more quickly into a foreign market.
- Scalability in the supply of products or services: It is important to have a product or service offering that can be adapted to the needs of different international markets, and that allows for rapid expansion and growth of the company. For example, a software company that offers its product in different languages and with specific features for each market can scale more quickly.
Scalability is important in any business seeking to grow and expand, and this also applies to companies seeking to internationalise.
Digitalisation, outsourcing, strategic alliances and scalability in product or service offerings are some ways to make a company more scalable and enable international growth.
Case study of scaling up the different parts of a business model
Suppose a cleaning services company wants to make its business model scalable.
Strategies to achieve this could include
- Process automation: Identify business processes that can be automated, such as appointment management and invoicing, and use technological tools to perform these tasks more efficiently and with fewer resources.
- Standardisation of services: Define a set of standard services that can be offered to customers in different locations and that do not require a large amount of customisation. In this way, consistent and standardised services can be offered to a larger number of customers.
- Use of technology: Use technology to improve the efficiency of cleaning services, such as sensors to monitor the cleanliness of buildings and robots to perform repetitive and heavy tasks.
- Geographical expansion: Identify new geographic markets and expand the business into those areas. This will allow the company to grow its customer base and increase its reach.
- Strategic partnerships: Establish strategic partnerships with other companies to offer complementary services to customers. For example, a cleaning services company could partner with a maintenance company to offer comprehensive services to customers.
In general, strategies to make a business model scalable, involve identifying processes that can be automated or standardised, using technology to improve efficiency and expanding the business into new markets or through strategic partnerships. The automation of a process is a way of making a part of the business model scalable, it is an investment that allows a cost to be reduced.
AUTOMATIZACIÓN
Automating a process is a strategy to make a part of the business model scalable, while at the same time it can reduce costs and improve productivity. By automating repetitive and manual tasks, human resources and time can be saved, allowing you to focus on higher value-added tasks and spend more time on innovation and business growth.
In addition, automation can help improve the quality and consistency of products or services offered, reduce errors and improve the customer experience. All of this can have a significant impact on a company's profitability and success.
It makes no sense to automate a task in a company that is not yet established. It is true that in the early stages of a business, it may not make sense to automate certain tasks because it is not yet consolidated and does not have a stable demand. In these cases, it is a mistake to invest in automation, even if you get some cost savings, you run the risk of losing the investment.
In addition, it is important to bear in mind that automation may require a significant upfront investment and that it may take time to see the benefits. However, It is also important to assess each specific case and determine whether automation can be beneficial in the long term. If it is a repetitive, time-consuming task that we are sure we have to perform, automation can reduce costs and increase efficiency in the future.
In addition, automation can free up time and resources so that employees can focus on more strategic tasks of greater value to the business.
When is the right time to automate a task?
In general, it is advisable to automate a task once it has proven its importance and has been fully integrated into the business process. It is better to wait until a sufficient amount of revenue has been generated to justify the cost of automation.
In addition, it is important to consider whether automation will positively affect the quality of the product or service offered, efficiency and productivity, as well as customer satisfaction.
In short, the right time to automate a task is when the investment in automation is justified by the return on investment in terms of efficiency, productivity and product or service quality.
Examples of companies that have made parts of their business model scalable that were not scalable to begin with:
- Airbnb: In the beginning, the founders of Airbnb personally visited the flats offered on the platform to take photos and write detailed descriptions. However, as the company grew, it became impossible to visit each flat in person. Instead, Airbnb automated the process of registering new flats and allowed the owners themselves to take and upload photos and descriptions of their properties.
- Uber: In its early days, Uber used a network of drivers in the city of San Francisco to provide the transportation service. However, with its rapid growth, Uber had to automate the driver selection process and allow people to sign up to be drivers through its mobile app.
- Dropbox: In its early days, Dropbox relied heavily on customer acquisition through word-of-mouth referrals. However, over time, the company developed an automated referral programme that allowed customers to recommend Dropbox to their friends and receive additional free storage on the platform.
- Amazon: In its early days, Amazon relied on a large number of workers to pack and ship customer orders. However, with its rapid growth, Amazon automated much of its warehousing and shipping process, allowing products to move automatically through its supply chain.
These companies have managed to make parts of their business model scalable that were not scalable to begin with by automating processes and implementing technology to enable greater growth and efficiency in their operations.
Some examples of activities that are not scalable:
- Personalised consultancy services that require personalised attention tailored to each client.
- Manual or craft jobs that require specific skills and cannot be automated.
- Services involving the physical presence of the entrepreneur, such as hairdressing, massage or physiotherapy.
- Services that depend on limited natural resources, such as fishing or mining.
- Time-consuming services, such as childcare or elderly care.
These examples are not necessarily negative or unviable, but require a redesign of the business model to make them scalable.
No business model is scalable at birth.
In general, it is true that no business model is scalable at birth, as scalability requires a systematic approach and a level of automation that can only be achieved with time and experience. However, there are exceptions to this rule, such as companies that are born as technology platforms or that use advanced technologies from the outset to automate and optimise their processes. In these cases, the business model can be scalable from the outset. But in general, For most companies, scalability is a goal that is achieved with time and experience.
How can you make a training service scalable?
Giving training hours is in principle not scalable.
To make a training service scalable, the following strategies can be considered:
- Creating digital content: Instead of face-to-face training, digital content such as videos, tutorials, online courses, webinars, podcasts, etc. can be created and made accessible anytime, anywhere. In this way, a wider audience can be reached and infrastructure and staff costs can be reduced.
- Automate processes: Administrative and logistical processes can be automated to reduce the time and costs associated with training management, such as enrolment management, timetable planning, student assessment, among others.
- Personalisation of training: Personalisation of training can help to improve the student's learning experience and increase their engagement with the learning process. To achieve this, technology can be used to create personalised curricula, offer virtual tutorials or create online discussion groups.
- Strategic alliances: Strategic alliances can help to increase the scalability of a training service, as you can collaborate with other companies or educational institutions to offer joint training programmes, share resources, tools and knowledge. We leave the non-scalable part of the business to them and the scalable part to us.
How to make an advisory and consultancy service scalable?
To make an advisory and consultancy service scalable, the following options can be considered:
- Create a training system: One way to make a counselling service scalable is to create a training system in which clients are trained in specific skills so that they can address some of the problems autonomously. This can include the creation of educational content, such as online courses, workshops and seminars.
- Standardise processes: Another way to make an advisory service scalable is to standardise the processes used to do the work. This involves creating templates, tools and tracking systems that can be used by any consultant or advisor. This makes processes more efficient and reduces the time spent on administrative tasks.
- Using technology: Technology can be a great help in making a consultancy service scalable. For example, video conferencing tools can be used to conduct virtual meetings, allowing consultants to work with clients anywhere in the world. Project management tools can also be used to organise work and ensure that the whole team is aligned.
- Create a network of partners: A network of partners can be created to expand the company's capacity to provide advisory and consultancy services. These partners can be other consultants or experts in the field who can bring additional knowledge and skills to the firm.
In general, to make an advisory and consultancy service scalable, it is important to focus on standardising processes, automating tasks and incorporating technology so that efficient and cost-effective solutions can be offered to a larger number of clients.
How can a business model of manual or craft jobs that require specific skills and cannot be automated be made scalable?
Although manual or craft jobs that require specific skills may seem difficult to make scalable, there are several strategies that can be used to achieve this.
STRATEGIES:
- Teaching: Instead of doing all the work manually, one way to make a craft business scalable is to teach the necessary skills to others. By training others to do what you do, you can expand your reach and gain more potential customers.
- Production process: It is important to analyse the production process to identify bottlenecks and areas where efficiency can be improved. If the production process can be optimised, lead times can be reduced and production can be increased, allowing the scope of the business to be expanded.
- Subcontracting: If there are certain parts of the business that cannot be automated or taught, you can outsource to others who have similar skills and can do the work efficiently. In this way, you can cope with increased demand without compromising the quality of the work.
- Product diversification: If the business is focused on a single product or service, it can be difficult to scale. Instead, it is possible to consider diversifying the offering by creating new products or services that attract new customers.
- Digitisation: In the digital age, many craft enterprises have managed to make their business model scalable through digitalisation. This can include selling products online, creating a platform to receive online orders and payments, as well as marketing through social media.
While manual or artisanal jobs can present unique challenges to scalability, there are several strategies that can help business owners expand their reach and grow their operations.
How can a business model for services involving the physical presence of the entrepreneur, such as hairdressing, massage or physiotherapy, be made scalable?
Services that involve the physical presence of the entrepreneur are more difficult to scale than digital services or automated solutions, but can still be made scalable in a variety of ways.
Strategies that can be employed include
- Training and education of other professionals: The entrepreneur can teach his or her skills to other professionals and establish a network of collaborators, thus expanding his or her reach and increasing demand-side capacity.
- Establishment of franchises: The franchise model allows the business model and brand to be replicated in different locations, which can increase the company's presence and reach.
- Technology implementation: While it is not possible to fully automate the service, technological tools can be used to improve the efficiency and quality of services offered. For example, online booking platforms can be used to schedule appointments and payments, and digital tools can be used to track clients.
- Diversification of services: Complementary or related services can be offered to increase the profitability of the business and reach a wider customer base. For example, a hairdressing salon could offer make-up services or the sale of personal care products.
- Price increases: If the service is of high quality and in high demand, the price of services can be increased to compensate for the lack of scalability and maximise profitability.
In summary, while services that require the physical presence of the entrepreneur are more difficult to scale, there are strategies that can expand the reach and increase the profitability of the business.
How can a business model for services that depend on limited natural resources, such as fishing or mining, be made scalable?
Scaling a service business model that relies on limited natural resources can be challenging, as the availability of these resources is limited and cannot be easily created or replicated.
However, there are some strategies that can be considered:
- Diversification: While the natural resource may be limited, it is possible to diversify the services and products offered to reduce dependence on a single resource. For example, a fishing company can diversify its product offering and also offer sightseeing tours or the sale of products derived from the sea.
- Technology and efficiency: More efficient technologies and practices can be implemented to make better use of limited resources. For example, a mining company can adopt more sustainable practices and technologies that allow for more efficient and less invasive extraction of the resource.
- Collaboration and partnership: Collaborations and partnerships can be established with other companies or local communities to share the use of the natural resource in a sustainable and equitable manner.
- Research and development: Investment can be made in research and development to find innovative ways of harnessing the limited resource and to develop derivative products and services that are more sustainable and cost-effective.
In short, making a business model that relies on limited natural resources scalable requires a combination of strategies to diversify supply, improve the efficiency and sustainability of resource use, establish collaborations and partnerships, and invest in research and development to find innovative ways to harness the resource. We talk about "scalability" when the revenue growth of a model does not need to be accompanied by a proportional increase in investments and expenses. I can double sales without doubling expenses or investments. I have to design every key activity (+) of my model to make it scalable. That is, I have to make most of my model scalable. See also the concept of leverage (+).
If you want to finance the growth of your company with the entry of a private investor, such as business angel (+) o venture capital (+), you have to demonstrate that, in addition to being viable and feasible, your model is investable.. That is, with a clear exit and a potential for growth and scalability. (see looking for a partner). Scalability is therefore a key and selective criterion for all investors, and it is also very useful for your company.
In graphical terms it could be represented as follows
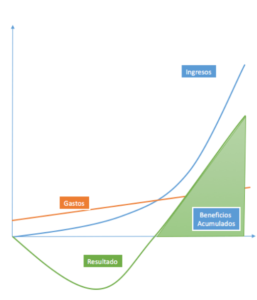
As we can see, there comes a point after the break-even point, or break even where revenues grow exponentially. However, expenditure grows in a linear fashion o, in case they grow exponentially, at a slower pace than revenues. Revenues are then decoupled from expenses "disproportionately" and make earnings growth exponential, like value creation. There are two competitive advantages (+) The economies of scale or the accumulated learning curve are very interesting. Many entrepreneurs have managed to design startups (+) or start-ups which, through the use of technology, grow quickly and rapidly while maintaining flexible and adaptable structures in line with market developments and at relatively low costs.
NOT all companies with high growth potential are scalable!!!
They are different concepts. A business model (+) can have a very high growth potential, even double-digit growth, but no such scalability potential. In the high scalability model, the benefits accrued as value generation are much higher than the benefits accrued in the growth model (without high scalability). In other words, over the same time horizon and similar cost structure, the scalable model generates higher value than a model with good growth potential but without significant economies of scale. This is why many investors require the business model to be scalable. So that value creation occurs quickly, and disproportionately (in the positive sense). Scalability in a Startup (+) improves the return potential for investors. In addition, a highly scalable model is likely to have a process of internationalisation (+) simpler as it will not require significant additional structures once it is already developed in the domestic market.
"Scalability" is used in technology to refer to the property of increasing the working capacity or size of a system without compromising the normal operation and quality of the system. A scalable system can increase the number of users, the number of data it processes or the number of requests it receives, without significantly affecting its speed of response.
EXAMPLE:
DNS New domains are created every day and the speed of access does not decrease. If new functions can be added to a product or system with minimal effort, the system is said to be scalable.
We recommend that you complete a acceleration week (+) to make your business model scalable!
Why do I need scalability in my business?
A scalable model earns a lot more money than a non-scalable model - for the same entrepreneurial effort you will live much better!!! The business angels (+) they only want scalable startups. The startup law (+) Spanish allows you to access many benefits if you manage to register your company as a startup with ENISA, for which you have to demonstrate that you are scalable. An entrepreneur needs to create a scalable company to ensure long-term growth and success. A scalable company allows you to increase your production and reach efficiently and without a proportional increase in costs, which allows you to increase profitability and valuation potential. In addition, A scalable business can also attract investors and facilitate a successful exit.
HERE ARE SOME TIPS TO HELP YOU CREATE A SCALABLE STARTUP:
- Identify a market need: Before starting to build the business, it is important to research and understand the needs and problems of the market.
- Focus on the solution: the company should focus on solving the identified problem, in order to make the solution as effective as possible.
- Building a strong team: A diverse team with complementary skills is crucial to the success of the company.
- Use technology to automate processes: automating processes will allow the company to operate in a more efficient and scalable way.
- Develop a sound growth strategy: Planning a long-term growth strategy is essential for the long-term success of the company.
- Remain flexible: being able to adapt to changes and evolutions in the market is essential for the scalability of the company.
- Identify and use appropriate resources: It is important to identify and use the right resources, be it finance, technology, personnel, etc., to support the growth of the enterprise.
During the mentorDay acceleration programme (+) learn how to take these steps properly.
TIPS ON HOW TO MAKE YOUR START-UP BUSINESS MODEL SCALABLE:
Business models are not scalable from birth, I would say that no project starts scalable, we always start doing everything manually (not automatic), by hand (without machines or programs), but you as an entrepreneur are responsible for creating a future action plan to make your model scalable... You do not start investing resources to make scalable until you have not validated and we are sure of the market potential. I'm making each of the key activities of my company (+). Sometimes, it is surprising how little imagination we show when it comes to building business models, either by imitating the one used by our competitors (great idea, so we compete with their rules!) or by introducing small changes without understanding the model as a whole... which is where the real power of this approach lies, in tackling it with a systemic approach.
WHAT LEVERS WE CAN USE TO CREATE A SCALABLE MODEL THAT WE CAN TRANSLATE INTO OUR BUSINESS PLAN:
Reduce your unit variable cost. One of the levers of a scalable business model, a consequence of fixed costs being fairly stable (or at least growing linearly) is to monitor as a key indicator (and try to minimise) the cost of materials sold (= UNIT VARIABLE COST)... which includes not only the cost of producing the product or service itself, but all the additional costs of putting the product in stock and selling it (from logistics costs to production costs). It is an indicator that reveals the variable cost of producing each unit.
IS EASY TO UNDERSTAND IF WE TAKE HOTEL ROOMS AS AN EXAMPLE:
Selling a night in a hotel room involves a more or less stable number of fixed costs ... but what is really decisive are the costs of materials sold, i.e. what it costs to "produce" (rent) a night in that room (as opposed to not doing so):
- Amenities (soap, shampoo, toothpaste...).
- Cleanliness of the room.
- Laundry (sheets, towels...etc.).
- Water, electricity, etc.
These are the numbers that are really evaluated by the hotel management when deciding whether to make a room available or not at X cost, as any income that covers these costs is better than having it empty... Los modelos de negocio en Internet, basados en la web, en software, o en aplicaciones móviles típicamente nacen con un grado de escalabilidad muy superior a un modelo de negocio basado en activos físicos, ya que aunque puedan tener unos costes fijos iniciales altos, su coste de materiales vendidos es muy contenido. De hecho, en algunos casos éste coste variable unitario se acerca a cero, (puedo atender a muchos mas clientes sin realizar más costes ni inversiones) lo que supone unos beneficios potenciales muy grandes…
But this does not mean that we cannot integrate scalability when designing the foundations of a new business model, whether offline or online. The key, undoubtedly, is in the design of the cost structure... and its dependence on human capital: a business model whose cost structure is heavily dependent on the work done by staff as a unit of revenue is not scalable.
WHAT ARE THE KEY VARIABLES?
SECTOR BANCA
However, it is not a losing battle if the company's business is not scalable. We can complement "offline" models with "online" models, to provide at least part of the business lines with scalable approaches. As an example, We can look at the banking sector, which has been able to take this step wisely: lBanking has traditionally relied on providing personalised services to each customer and, therefore, not scalable in its bank branches (people in the role of tellers) to serve its customers. Several years ago, automated teller machines (ATMs) were introduced to try to alleviate the burden on employees acting as tellers and, more importantly, to start to make a non-scalable model scalable. But the model was still not very scalable, as it depended on the number of ATMs deployed and their location. To finally break the famous resources=revenue lock-in, online banking was deployed... which finally made the number of customers served reasonably independent of the resources invested in serving them, as it is based on a platform". The above example gives us one of the main keys to making a business model scalable: design and look for self-service processes where customers can lower some of the fixed costs we have in our business model. Another example is e-commerce systems or mass customisation strategies, where customers are allowed to interact with systems that offer them customisation, but automatically and with little or no consumption of their own resources! artificial intelligence (see+ TIP).
Examples of businesses that have used this strategy include:
"Some iron sales companies have complemented their traditional business model, where the customer buys plates, beams and iron elements in customised sizes through a sales force, with a website where the same elements are offered at a much better price with standardised sizes, and where the customer can customise only a few attributes and order online.
Another key to designing scalable business models is undoubtedly the ability to anticipate: the fact that scalability offers a linear and controllable margin of growth in the cost structure has an important implication:
"If we are not able to foresee the growth (or decrease) needs of the cost structure, we will not be able to provide service... possibly implying problems with the revenue stream".
Let us imagine that Facebook (+), as a paradigmatic company of a scalable business model, does not correctly dimension its most important resources (its servers) and a peak load occurs that causes the platform to fall... it is certainly a situation that I am sure Mark Zuckerberg would not want to live. This has another important implication, but in the opposite direction: we do not want to have idle production capacity as a result of having oversized in anticipation of a possible but not probable future peak, as this implies costs that we could delay in time. It is just as important not to undersize as to oversize. This means that we must design processes, indicators and thresholds capable of giving a certain amount of advance warning of the future need for resources to support the business model.
The key to a scalable business model is therefore adaptation, and therefore, it must be able to scale down as easily as it scales... although obviously we must design it for growth. In this scenario, our obsession must be to achieve economies of scale where growth not only does not generate more structure, but also reduces production costs. "For example, it is typical that we get much better prices from our suppliers when we handle large quantities of purchases, or we can manufacture much cheaper the more we produce (up to the famous limit we mentioned before...)".Finally, and as a consequence of the thesis I am defending, the business model must be considered as a whole... It is therefore possible to design changes in some of its dimensions to enhance scalability: The revenue strategy you choose can boost your scalability (or sink it, if you choose the wrong one).
For example, subscription-based revenue strategies enhance the scalability of the model, as they make it possible to have:
- Demand forecasting
- Economy of scale, as better prices can be negotiated with suppliers
- Negative cash flows (NOF): customers pay in the short term (cash/30 two) and suppliers are paid at a longer term, so the business is cash generative.
CONSEQUENTLY, AND SUMMARISING THE ABOVE, THE KEYS TO A SCALABLE BUSINESS MODEL ARE AS FOLLOWS:
- Self-service.
- Anticipation.
- Dimensioning.
- Economies of scale.
- Revenue strategy.
There are many examples of businesses that base their competitiveness on how they have innovated their business model, and many of the traditional models are making or have made the transition to scalable models: auctions, direct sales, brokers, banking, editorial publications, media, recruitment... De todas formas, y como siempre, pongamos el foco donde es necesario: es una estupenda idea el diseñar un modelo de negocio con la escalabilidad como característica base… pero si no somos capaces de generar demanda y crear flujos de ingresos importantes y recurrentes, no servirá de nada.
SO IS IT NOT POSSIBLE TO MAKE A SERVICE BUSINESS SCALABLE?
By definition yes, but we can adopt a series of guidelines to at least try to make them somewhat more scalable, mainly by trying to standardise the services as much as possible, optimising them and making them as procedural as possible... but in my personal opinion it is a bad way to go for training services, consultancy... etc. Since it can lead us to offer our clients "canned" approaches that in the end manage to commoditise our services. I particularly believe in the more artisanal approach, as described in the artisanal consultancy statement. Having said that, I would not want to close without trying to break the belief that service-based models are not scalable, using as an example the approach adopted by Alex Osterwalder (author of the essential book "Business Model Generation" and father of the business model canvas),
Ostwewalder has managed to complement a business model that is not scalable by definition (consultancy, conferences, training) with elements that are scalable and reinforce its value proposition:
- Sale of a book.
- iPad application.
- Sponsors.
APPLY THIS TIP TO YOUR PROJECT
TASK
Now that you have read the TIP, answer these questions:
- Do you have great potential for customer growth?
- What are your bottlenecks?
- Can you double your customers without doubling your costs?
- Which activities in your model are scalable today and which in the future?
QUIZ
- 💻 PRACTICE with an expert in the next practical webinar.
- 🔎 CONSULT more related TIPs with this same theme.
- 📖 AMPLIA your knowledge by downloading this EBOOK y this EBOOK.
THINK ABOUT YOU
- 🚀 IMPULSA your company in the next acceleration programme, ¡book your place now!
- 🥁 PRACTICE with your project in this practical webinar, ¡apply for your place!
- 🌐 CONTACT with other entrepreneurs and companies, ¡register and take part in the next Networking!
THINK ABOUT HELPING OTHERS
- 🤝COLLABORATE as a volunteer: expert, mentor, inverter, awarding, Spreading the word, challenging, innovating, creating a TIP...
- 💬 RECOMMENDS this programme to reach out to more entrepreneurs by Google.
- 👉 SHARE your learning!
- 📲 SEND this TIP 👇
Rate this TIP!
Click on the stars to rate
Rating "79" - Average " - Average4.6"
No votes yet, be the first to vote!
We are sorry you did not find it useful.
Help us improve this TIP!
Leave us a comment and tell us how you would improve this TIP











[...] A business model is the mechanism by which a business attempts to generate revenues and profits. The model is the way of doing business, by which a company generates revenue in a profitable, recurring and scalable manner. [...]
[...] For your business to be successful, it is essential that you are very clear about your customer segment and that you focus all your efforts on satisfying them correctly. Finding what they have in common will allow you to grow and scale. [...]
[...] Ultimately, the whole lean startup methodology focuses on the company, before running out of resources, coming up with a plan that works; in Blank's words, that creates "a repeatable and scalable business". [...]
[...] How to make the company scalable? [...]
[How much is a glass of water worth? If I am in the desert about to die of thirst, how much am I willing to pay? The price varies according to the perceived value at any given moment. When we sell online, we can't be in front of the negotiating table because we would lose scalability. [...]
Growth Potential vs. Scalability Potential
Interesting TIP that values scalability and with which we will agree as long as it increases its capacity and manages to cover a higher demand without losing quality.
for Mentordy.
I am satisfied with the teachings and methods and every day the tips are of great help.
I am Ecuadorian with my project to reside in Spain to manage the business I am launching.
JUlio for us to help you to settle in Spain you must register and complete this programme. https://mentorday.es/softlanding/