Propuesta de valor - Canvas
Índice
When designing our business model, the most important aspect and the one that generates the greatest uncertainty is the value proposition. Being able to find a criterion that confirms that what we are doing makes sense to the client is critical. In this part of the CANVAS you have to validate the solution that you have designed for the problem or need (+) of your customer segment (+). Once we have detected the problems or needs of a customer segment, then, we proceed to find a solution for them and at the end we will formulate the proposal with a short sentence, addressed to the customer segment to be addressed, in which we will expresses clearly and concisely what we offer to solve a problem or meet a need.
We will design a different value proposition for each customer segment. That proposition has to be sufficiently attractive to make the customer want to pay. We cannot analyse our value proposition in a vacuum, as we should take into account a basic element for any type of business: the customer, since, the success of any business model, it is based on the good relationship between these two elements:
- The value proposition.
- The needs of the client.
The value proposition is the sum of the values provided by the key activities.
It is therefore key to analyse the product-market fit in which we identify a product/service that fits perfectly with a defined and validated market.. But how do I assess whether what I am doing really makes sense or not? The answer is simple: If customers buy your product/service.
WHAT IS THE "VALUE PROPOSITION CANVAS" BASED ON?
It is based as we have mentioned on matching the needs of your customer segment with your value proposition, and to understand how it works the first thing to know is that we are going to work in four distinct phases:
Phase 1: OBSERVATION
At this stage, we need to understand the real needs of the client, and market research and similar tools are of no use to us. They can be activities of daily working or personal life. Identify the basic activities or tasks of our clients. The objective is to find a problem or need to be solvedThe following list is a fairly promising list of what, after observing clients, we believe to be their main needs. Detect any frustrations or negative emotions before, during or after. Analyse the benefits and what the customer will receive from using, buying, renting, etc. our product or service.
Phase 2: DESIGN
Instead of doing what we always do, which is to design first and then see who can use it, this time we will work the other way around: first we identify a problem worth solving, and then we will see how we solve it.
Phase 3: VALIDATE
Up to this point what we have achieved is to identify mainly two things: customer hypotheses and value hypotheses. Once the hypotheses have been identified, it is time to check (validate) in the real world whether what we have imagined is true, i.e. it is time to convert the hypotheses into certainties. The way to do this is going out on the street and talking to the customer validating or discarding the customer hypotheses we have created. We should build a minimum viable product (or service), take it to market to a specific group of customers and see how they react to our value proposition.
- Client hypothesis: What we think the client needs. The problem we think he wants to solve.
- Value assumptions: what we believe will solve the client's problem or need.
Phase 4: ADJUST
The next step, based on the findings of the validation process with the client, will be to readjusting our value proposition. In this adjustment phase, the value hypothesis will be reconsidered based on what has been learnt with the real customer. In this phase and with what we have learned from the client, we will proceed to the construction of the first prototype of the product, the minimum viable product that will help us to validate and adjust our value proposition.
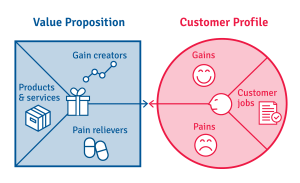
In formulating our value proposition, we must be able to respond clearly:
- ¿What are we creating?
- For whom? Customer segment.
- ¿What does it solve? Problem, need.
- ¿Why you are going to be chosen and not the rest? Differentiation from the competition. If the proposal does not differentiate you, you will have to be the cheapest. If we offer the same as everyone else (if we don't differentiate ourselves); why would a customer buy if our prices are not the lowest in the market?
- What benefits we contribute?
Features of the proposition that bring benefits and value to the segment:
PERSONALISATION
- Complete adaptation of our products or services to the specific needs of a customer segment.
- The solution can be tailored to meet the particular tastes or needs of each client.
FUNCTIONAL DESIGN / USABILITY
- Making things easier or more practical can also be a source of value.
PRICE (BASIC PROPOSAL)
- Offering similar value at a lower price is a practice that can have important implications for all other aspects of your business model.
- Offer the same solution at a lower price than the competition.
COST REDUCTION
- It consists of helping your clients to reduce their costs by using your product/service.
- The proposal is to optimise expenses in order to minimise the total cost in production processes or other businesses.
-
- New atif the proposal addresses problems or needs that had not yet been identified.
- Qualitywhen the qualities of our products or services are better than those of our competitors.
- Convenience: facilitating clients' activities and minimising efforts.
- Brand / Statuswhen you want to establish a fashion or trend in the customer segment.
- PerformanceThe proposed solution fulfils its purpose in a superior way or with higher performance than that offered by other solutions.
- Risk reductionby adopting our solution, the customer will have a lower risk than with the competition. For example: financial, social or environmental.
- Design: las características artísticas de la solución son las que principalmente definen la propuesta
What makes a good value proposition?
A good value proposition is not just about the product or service itself. The value proposition is not only the description of the product or the attributes of your service, differentiating it from the commercial offer, it is value provided to the customer...
THE VALUE PROPOSITION IS A WHOLE THAT MUST ALSO BE CONSIDERED:
- After-sales service for products and services.
- Post-training consultancy or delivery of a report.
- Free delivery / immediate delivery especially in the case of products.
- Free maintenance (e.g. a website).
- 24/7 customer service.
I think it is becoming clearer that the concept of value proposition and why we often talk about unique value proposition (UVP).
THE EXAMPLE OF AMAZON:
An example of added value which offers Amazon as well as selling books and other products in its online shop:
- Protects publishers and authors of fraudulent sales through online channels (PUV on the supply side).
- It offers a review and rating system of the products offered in the online shop (PUV on the demand side).
What a value proposition is NOT:
- No is a slogan commercial or advertising.
- No are the visionThe company's mission and values.
The mistake we have all made is ever thinking, dreaming or designing a product or service without having looked at the needs or problems of consumers (actual or potential). REMEMBER: fall in love with the solution to your customer's problems, don't fall in love with your product (a typical mistake of very technical entrepreneurs).
Eliminate problems...
The value proposition should solving a problem for our customers potentials. This is what Blank calls Pain Killerssomething like "pain reducers"...
OUR VALUE PROPOSITION MUST:
- Reducing the cost of money, time or effort to perform a task.
- Make the customer feel better.
- Correct or improve tools which do not work well at present.
- To solve everyday problems.
- Facilitate things.
- Enhance prestige, trust or status of our clients.
- Reduce risk: social, technological or financial.
A value proposition containing any of these benefits, will make customers buy from us or at least rate us above the competition when it comes to make the decision to buy.
MEETING A NEED
A product or service may not solve a problem but rather to satisfy a need.
Two clear examples of satisfying a need are:
- Instagram. Before it was created, did we really have a problem sharing our photos with our friends and the rest of the world? If your answer is NO, it's because Instagram satisfies the basic and instinctive human need to communicate, only it does it with digital technology and in a global way.
- iPhone. If the iPhone had only solved the need for communication, it would not have been what it is today, because at the time of its launch there were mobile phones on the market. The real revolution of the iPhone focused on satisfying our need for entertainment and information. A real pocket computer that allows us to have a browser (browser) + games, music, and in the process it communicates; just like any other phone. Today it covers our status needs as all other devices have imitated its functionalities.
CARACTERÍSTICAS DE UNA PROPUESTA ÚNICA DE VALOR ATRACTIVA:
- It is the core and fundamental pillar of a well thought out and executed business model.
- It focuses on solving problems or meeting needs of customers.
- It focuses on what the client wants and not on what we want.
- This is a unique feature that our competition cannot imitate.
- It acts as a barrier to entry because it is difficult to copy.
- It is not just about offering a feature in a product, but focuses on issues such as emotional and social of customers.
VALIDATE THE VALUE PROPOSITION:
It is a matter of adjusting the value proposition based on the product and customer fit. After all, everything we have so far is hypothetical, they are only ideas until they are validated with our client:
- Client hypothesis: what we believe The problem we think the client needs. The problem we think he wants to solve. We have to discover the real problem or the real need he has!
- Value assumptions: what we believe that will solve the customer's problem or need.
Durante la validación vamos pivotando la propuesta (adaptando, ajustando, mejorando) hasta conseguir que aporte el valor suficiente para que el cliente quede satisfecho y este dispuesto a pagar.
HOW TO VALIDATE A VALUE PROPOSITION?
In the methodology lean we are following, the only way to validate a value proposition is by "getting out of the office and talk directly to the people in the customer segment. And this is something we as entrepreneurs have to do, it is not delegable! We must build a minimum viable product MVP (+), to take it to the market for a specific group of customers and see how they react to our value proposition, i.e., how they react to our value proposition, do experiments. All the changes that customers perceive as necessary must be assessed by us for inclusion in the new revised and amended value proposition. All characteristics not perceived as value-adding The Lean methodology treats them as merely a waste of time or money in the production process, and the customer's feedback will be eliminated from our product or service if they generate a waste of time or money during production. Lean methodology treats them as mere waste (of time, money or effort).
Examples of Value Propositions
TO EXPLAIN HOW TO IMPLEMENT A VALUE PROPOSITION IN REAL LIFE, WE WILL USE SOME EXAMPLES FROM WELL-KNOWN COMPANIES:
STARBUCKS

The coffee giant's value proposition recreates an experience around coffee and how it relates to the consumer's life. The three most important aspects of the value proposition are:
- Coffee: master the different stages of the supply chain, such as cultivation, roasting and distribution logistics.
- The environment: comfortable cafés, relaxed atmosphere, soft music and WiFi internet connection.
- The service: offers a personal and intimate relationship with customers.
Starbucks offers an experience around coffee, they have leveraged it and have become world leaders in their sector. The company has invested a lot of money and effort to make the value proposition penetrate the consumer's mind.
Here you have the Starbucks business model (+) in detail.
SODA STREAM

It is a company that sells a machine to prepare soft drinks at home. Its value proposition is based on:
- You have a soda machine at home.
- Making soft drinks is easy and fun. Anyone in the family can make their own drink. The promotional image shows four family members (parents and two children).
- The machine is eco-friendly and environmentally friendly. The company claims it helps save 2,000 bottles every year.
- They offer colourful bottles designed for children.
Soda Stream has managed to clearly differentiate itself from traditional soda companies such as CocaCola and Pepsi. The ad is very original and funny, as the competitor's bottles explode when the soda machine is used.
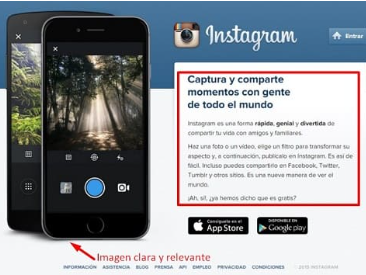
The photo and video sharing app explains the value proposition on its website. In a short paragraph they describe everything they offer and the benefits the user will receive. It is an excellent example of how to convey a value proposition in a short paragraph.
The most important points to highlight on the Instagram website are:
- The title shows the value that the app offers.
- The text explains how the app works, including the functions for adding filters to photos and videos.
- The mobile image enhances the promotional text.
ZARA

As a globally known brand, Zara does not need to publish its value proposition. In fact, Zara's homepage does not feature the proposition, but rather the site is dedicated to showcasing the brand's sobriety and attractive designs. The focus of the value proposition is to offer excellent quality clothing at affordable prices. Its concept is based on absorbing market trends and launching new designs very frequently.
Here you have in detail the Zara's business model (+).
Caso Práctico: Mentoría sobre Triple Propuesta de Valor con MentorDay
Context: Juan es un empresario que acaba de lanzar su nueva empresa de servicios de consultoría empresarial. Está buscando diferenciarse en un mercado competitivo y busca la ayuda de MentorDay, una empresa especializada en mentoría empresarial, para desarrollar una propuesta de valor única y atractiva.
Primer Encuentro: Definiendo Objetivos MentorDay organiza una primera reunión con Juan para comprender mejor sus objetivos y visión para la empresa. Juan explica que su objetivo es destacar en el mercado ofreciendo servicios de consultoría que realmente marquen la diferencia para sus clientes. Quiere una propuesta de valor que no solo atraiga a nuevos clientes, sino que también retenga a los existentes.
Análisis de la Situación Actual: MentorDay realiza un análisis exhaustivo de la empresa de Juan, identificando sus fortalezas, debilidades, oportunidades y amenazas. Durante este proceso, se destacan tres elementos clave que podrían formar la base de una triple propuesta de valor: experiencia especializada, enfoque personalizado y resultados tangibles.
Desarrollo de la Triple Propuesta de Valor:
-
Experiencia Especializada:
- MentorDay sugiere que Juan se enfoque en la experiencia especializada de su equipo. Pueden resaltar la formación y experiencia única que poseen en áreas específicas de consultoría empresarial, brindando a los clientes la seguridad de estar trabajando con expertos.
-
Enfoque Personalizado:
- MentorDay aconseja a Juan centrarse en ofrecer soluciones adaptadas a las necesidades individuales de cada cliente. Esto implica un enfoque personalizado en el que se comprendan a fondo los desafíos y objetivos de cada cliente, permitiendo un servicio más efectivo y orientado a resultados.
-
Resultados Tangibles:
- MentorDay destaca la importancia de demostrar resultados tangibles. Se sugiere a Juan implementar métricas claras y KPIs para evaluar el impacto de sus servicios. Esto no solo proporcionará transparencia a los clientes, sino que también respaldará la eficacia de la consultoría de Juan.
Implementación y Seguimiento: MentorDay trabaja junto a Juan para implementar la triple propuesta de valor. Se desarrollan materiales de marketing que comunican claramente estos tres elementos a los clientes potenciales. Además, se establecen procesos internos para garantizar que la experiencia del cliente esté alineada con la propuesta de valor.
Results: Después de la implementación, Juan experimenta un aumento en la atracción de nuevos clientes y una mejora en la retención de clientes existentes. La triple propuesta de valor ha diferenciado a su empresa en el mercado y ha establecido una base sólida para el crecimiento continuo. MentorDay sigue brindando apoyo para ajustar y expandir la propuesta de valor a medida que la empresa evoluciona.
APPLY THIS TIP TO YOUR PROJECT
TASK
Now that you have learned about the Value Proposition - CANVAS, you should know how to answer these questions:
- What is your value proposition to each customer segment?
- How is the solution you have designed to meet the needs or problems of your customer segment?
- What benefits do they bring to your customers?
- What tests, trials or validations have you carried out with real customers to be sure they are willing to pay for your solution?
We encourage you to do the exercise of answering them!
QUIZ
- 💻 PRACTICE with an expert in the next practical webinar.
- 🔎 CONSULT more related TIPs with this same theme.
- 📖 AMPLIA your knowledge by downloading this EBOOK y this EBOOK.
THINK ABOUT YOU
- 🚀 IMPULSA your company in the next acceleration programme, ¡book your place now!.
- 🥁 PRACTICE with your project in this practical webinar, ¡apply for your place!.
- 🌐 CONTACT with other entrepreneurs and companies, ¡register and take part in the next Networking!
THINK ABOUT HELPING OTHERS
- 🤝COLLABORATE as a volunteer: expert, mentor, inverter, awarding, Spreading the word, challenging, innovating, creating a TIP...
- 💬 RECOMMENDS this programme to reach out to more entrepreneurs by Google.
- 👉 SHARE your learning!
- 📲 SEND this TIP 👇
Rate this TIP!
Click on the stars to rate
Rating "75" - Average " - Average4.9"
No votes yet, be the first to vote!
We are sorry you did not find it useful.
Help us improve this TIP!
Leave us a comment and tell us how you would improve this TIP











[...] are: a low-risk and high-potential alternative to sell and above all to confirm that our value proposition has a market. With prudence and strategy I recommend that you [...]
[Value proposition: [...] 2.]
[...] value perceived by the customer is achieved through the key activities that make up the value proposition and that we have designed in our model to cover their needs or solve their problems.
[...] revisions of the hypotheses captured on the canvas, the perfect fit between a value proposition and the customer segments is achieved [...].
[...] You must identify the type of product you want to sell or produce abroad. In particular, you must analyse and identify if the product needs to undergo some modifications, in order to adapt to the characteristics of the market (or markets) in which you are going to sell it (see this tip on value propositions) [...].
[...] offers from the competition... you have to be permanently in touch to adjust your value proposition, continuously measure your [...]
Very well summarised and helpful tip
Keys to success for the development of a project, a clear definition of a PROBLEM, in order to propose a SOLUTION that ADDS VALUE and customer satisfaction, if so, the COMPANY that derives such a solution will be a SUCCESSFUL COMPANY.