THE LIFE CYCLE OF A PRODUCT
Accelerate your business with these expert tips on "Product Life Cycle". Analyse and discover this TIP!
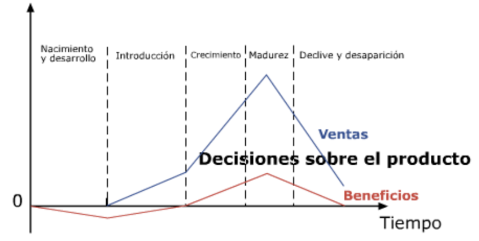
The life cycle of a product ands a marketing tool that describes the stages a product goes through from its introduction to the market until its decline and withdrawal. It is divided into four main stages: introduction, growth, maturity and decline. At each stage, the product has different characteristics and presents different opportunities and challenges for entrepreneurs.
STAGES
- Introduction: is the initial stage when the product is launched on the market. Sales are low and costs are high due to investment in research and development, advertising and promotion. Consumers are unfamiliar with the product and there may be concerns about its quality and value.
- Growth: At this stage, sales begin to increase as consumers begin to learn about the product and its value. Costs decrease as production is optimised and advertising focuses on establishing the brand. Product improvements occur and the target market expands.
- Maturity: At this stage, sales peak and begin to stabilise. Production costs fall further due to experience and economies of scale. Competition is strong and prices may fall. Entrepreneurs look for ways to differentiate their product to maintain their position in the market.
- Decline: At this stage, sales begin to decline due to competition from new or substitute products. Entrepreneurs must decide whether to withdraw the product from the market or find a way to revive demand through marketing strategies or product improvements.
It is important for entrepreneurs to understand the life cycle of their product in order to properly plan marketing and development investment, as well as to identify opportunities and challenges as their product evolves in the marketplace.
What is the difference between the product life cycle of a startup and that of a company?
The life cycle of a startup product and the life cycle of a company product do not differ significantly in terms of the general stages they go through. Both will follow a similar trajectory spanning four main stages: introduction, growth, maturity and decline. However, the difference lies in the duration and scope of each stage depending on the size and experience of the company. For a startup, the introduction stage can be longer and require more effort in terms of investment and marketing to generate awareness and adoption of the product. The growth stage can also be faster and more aggressive for startups as they seek to gain market share and expand into new geographic areas or customer segments.
On the other hand, for an established company, the introduction stage may be shorter, as it is likely to already have a customer base and a market presence. The growth stage may also be more gradual and focused on consolidating its market position. In a nutshell, While the product life cycle of a start-up and a company will follow the same general stages, the duration and intensity of each stage may vary depending on the size, experience and previous success of the company.
Practical examples from the product life cycle
Here are some practical examples of the product life cycle:
MOBILE PHONES
- Introduction: When the first mobile phone was launched, it was considered a luxury item and was only available to a few.
- Growth: Mobile phone technology developed rapidly and became an essential element in most people's daily lives.
- Maturity: the mobile phone market has become saturated with multiple choices and competition has intensified, squeezing profit margins.
- Decline: Due to market saturation and declining profits, manufacturers have started to diversify their product lines to remain competitive.
FOOD PRODUCTS
- Introduction: When a new food product is launched, a large investment in marketing and advertising is made to generate interest and demand.
- Growth: As the brand and product become better known, demand increases and so does revenue.
- Maturity: when the brand and product are established, competition increases and demand stabilises.
- Decline: when products become less popular or are replaced by newer or healthier alternatives.
VIDEO GAMES
- Introduction: When a new video game is released, there is a lot of buzz and players buy the game at full price.
- Growth: As the game becomes more popular, improvements and expansions are made to keep players interested and willing to pay more for the game.
- Maturity: after several expansions have been released, the market for the game becomes saturated and demand decreases.
- Decline: the game becomes obsolete and is replaced with a new, more popular and updated title.
What is the life cycle of a product in an internationalisation process?
The life cycle of a product in an internationalisation process may be similar to the life cycle of a product in a local market, but may vary depending on cultural, economic, legal and political factors in the foreign market where the product is being introduced. In the introduction stage, the product may require modifications in its design and features to adapt to the preferences and needs of the foreign market. In the growth stage, the product may experience an increase in demand as it gains market acceptance.
In the maturity stage, the product may face increased competition from other similar products in the foreign market. In the decline stage, the product may be replaced by newer and more advanced products, especially if the foreign market is undergoing rapid technological change. It is important for entrepreneurs and companies to take into account the cultural and economic differences in the foreign market, and to adapt their marketing and sales strategies accordingly to maximise the chances of success at each stage of the product life cycle.
Why is it necessary for an entrepreneur to know the life cycles of his products?
It is important for an entrepreneur to know the life cycles of his products because it allows him to understand where his product is in the market and to adjust his strategy accordingly. By knowing the stages of a product's life cycle (introduction, growth, maturity and decline), the entrepreneur can anticipate changes in demand and competition, adjust his marketing approach, modify his design or add features to maintain product relevance and maximise profitability.
It can also help the entrepreneur to plan the introduction of new products or the improvement of existing ones in order to remain competitive in the market. In a nutshell, knowledge of the product life cycle is crucial for informed and effective decision-making in an entrepreneur's business strategy.
How can an entrepreneur recognise the stage of his product well?
In order to recognise where a product is in its life cycle, the entrepreneur must carry out a thorough assessment of the market and the situation of his product.
Some ways in which you can identify the life cycle stage of your product are:
- Sales analysis: a drop in sales or slow growth could be a sign that the product is reaching maturity or decline.
- Competitive analysis: if there are many competitors in the market, the product could be in a stage of maturity or decline.
- Innovation analysis: If product improvements are being made, it may be in the growth stage. If there are no more innovations, it could be in the maturity stage.
- Price analysis: if the price of the product is declining, it could be in the decline stage.
- Profitability analysis: If the product remains profitable, it may be in a growth or maturity stage, while if costs exceed revenues, it could be in the decline stage.
In a nutshell, In order to recognise the stage of his product, the entrepreneur must be attentive to market signals and carry out regular analyses to determine the stage of his product in the life cycle. This will enable you to make the right decisions for the future of the product and your company.
At what stage of a product's life cycle is it common for improvements and modifications to be made to the product's design and features?
The stage where it is common for improvements and modifications to be made to product design and features is the growth stage. At this stage, the product has been accepted in the market and is experiencing increased sales, allowing the company to invest in improvements and modifications to remain competitive and meet consumer needs.
What is a common strategy to maintain sales and profitability of a product in its declining stage?
A common strategy to maintain sales and profitability of a product in its declining stage is to reduce production costs and increase marketing and promotional efforts to maintain its market presence and attract remaining loyal customers. Also diversification strategies can be considered, such as introducing new versions or variations of the product, or exploring new markets or distribution channels.
APPLY THIS TIP TO YOUR PROJECT
QUIZZES
- 💻 PRACTICE with an expert in the next practical webinar.
- 🔎 CONSULT more related TIPs with this same theme.
- 📖 AMPLIA your knowledge by downloading this EBOOK.
THINK ABOUT YOU
- 🚀 IMPULSA your company in the next acceleration programme, ¡book your place now!.
- 🥁 PRACTICE with your project in this practical webinar, ¡apply for your place!.
- 🌐 CONTACT with other entrepreneurs and companies, ¡register and take part in the next Networking!
THINK ABOUT HELPING OTHERS
- 🤝COLLABORATE as a volunteer: expert, mentor, inverter, awarding, Spreading the word, challenging, innovating, creating a TIP...
- 💬 RECOMMENDS this programme to reach out to more entrepreneurs by Google.
- 👉 SHARE your learning!
- 📲 SEND this TIP 👇