Cause-effect diagram. Fishbone. Ishikawa diagram for entrepreneurs.
With this diagram you can identify which causes are directly affecting the problem you want to solveYou can prioritise which is the most important and with the Kaizen method start applying short and permanent actions to achieve the change you want.
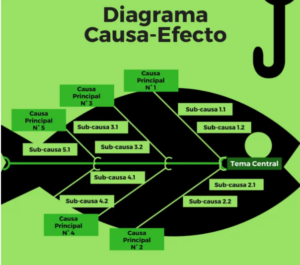
It is also called "Fishbone", because from the central theme the causes and sub-causes that originate it emerge in the form of thorns.
The Cause-Effect Diagram helps entrepreneurs to solve problems that may arise in their working life, although it can also be applied in the social and everyday sphere. Its application allows the best decisions to be made, after making a preliminary study of the barriers in front of us.
We owe this causal diagram to an expert Japanese business manager by the name of Kaoru Ishikawa, hence it is also known as the "Ishikawa Diagram". It is also known as the Fishbone because of its shape. In short, it is a tool for analysing problems and solutions that can arise in any company.
In this example the entrepreneur differentiated four categories of problems, as causes of the main problem of defects:
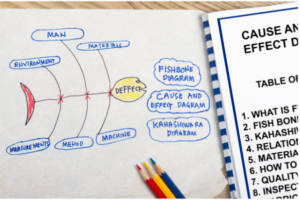
- People.
- Materials.
- Machinery.
- Methods or processes.
The Cause-Effect diagram is a simple graphical representation, which, as we have pointed out, is in the form of a fishbone. In the head would be the PROBLEM. And in each thorn the CAUSES that provoke it. Each thorn can have other smaller thorns, thus dividing the causes and sub-causes of the problem.
We start with a blank piece of paper to make a brief introduction of the problem we are going to analyse in the company.
Then we will draw the causal diagram in the shape of a fish skeleton.
Next, we will have to identify the main causes of that problem and place them in the thorns as categories (these are the ones we have previously pointed out as Person, material, machinery and method).
We have to ask ourselves the question: why has this cause arisen? And we will point out the sub-causes, which in the diagram, is the drawing of the branches of minor thorns.
We identify secondary and root causes. We make sure of those that can be corrected immediately.
Those causes/sub-causes that are not in our hands, we will pass them on to a person who is able to solve them.
Once corrections have been made to all the root causes of the problem, it is time for ANALYSIS and EVALUATION of the decisions that have been taken.
You can also consult other Related TIPs.
Learn more about mentoring by downloading this free EBOOK.
Do you want to help an entrepreneur by sharing your experience as a MENTOR? get accredited now.
Are you an entrepreneur? If you need support to boost your business, apply now for your mentor.








