
INNOVATION STRATEGIES, INNOVATION AMBITION MATRIX
Accelerate your business with these expert tips on "Innovation Strategies". Analyse and discover this TIP!
Defining an innovation strategy allows the company to identify what it wants to do and where it wants to go with innovation.
It is a framework for the whole organisation, that aligns objectives and actions to ensure that all efforts invested are commensurate with the level of risk taken and that work is carried out in the selected areas to achieve growth objectives.
The "Innovation Ambition Matrix" is an tool developed by Bansi Nagji and Geoff Tuff which helps companies to allocate funds among different growth initiatives and is a refinement of the of the "Ansoff Matrix".
Place on the X-axis the novelty of the company's offer. and in the axis AND the novelty of customers and markets to which the company has access. On each axis, three levels of distance are determined; existing (core), adjacent and totally new (transformational).
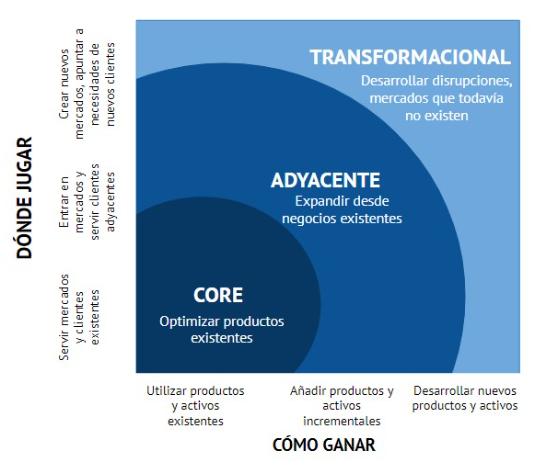
Innovation Ambition Matrix. B. Nagji and G. Tuff
Core-additive innovation is focused on the processes and products of the current business and the "transformational" one focuses on other customer segments (see TIP) or markets by offering new business models (see TIP)
Top innovation performers are those that have struck a balance between innovation focused on their core (see TIP), in adjacent and transformative initiatives and that, in addition, they have put the necessary tools and skills to manage the various initiatives as part of an integrated whole.
It is key understand and identify the differences between them, since, core/adjacent" allows for the evolution of current performance but does not meet the needs of the future. It is mandatory approach to "transformational" innovation when 5-year objectives are not feasible to achieve of the company with the expected business results in the same period.
There are three factors to consider when setting the investment allocation in the company:
- The type of industry. Manufacturing companies are likely to spend more on core than technology companies where a focus on transformational is a must.
- Competitive position. Small companies focus on "transformational" in order to create disruption and leading companies focus on "core/adjacent" in order to maintain their position.
- The time of development of the company. Start-ups will focus heavily on "transformational" innovation while mature companies will do the opposite.
References in this link (+)
The Innovation Ambition Matrix
The Innovation Ambition Matrix is a strategic tool that helps organisations to identify and plan different types of innovations. This matrix classifies innovations in different quadrants according to two key dimensions:
- Business impact: This refers to how innovation affects the organisation in terms of revenue, market positioning, efficiency, etc.
- Novelty of innovation: This aspect assesses the degree of originality of the innovation. It can be something completely new in the industry or a small improvement on an existing process.
Matrix Quadrants
- Incremental Innovation: This quadrant focuses on small but effective improvements to existing products or processes. The impact is relatively low, but so is the risk.
- Radical Innovation: Here we are dealing with transformational changes that have the potential to revolutionise the market or industry. The impact on The business is extremely high, but so is the risk.
- Process Innovation: This quadrant seeks to improve internal efficiency through process optimisation. Although the novelty is low, the impact on efficiency and costs can be significant.
- Business Model Innovation: This quadrant involves changes in how the organisation creates and captures value. It may be through new distribution channels, new pricing structures, or even entering new markets.
Internal Innovation Management
Internal innovation management is crucial to ensure that innovative ideas become reality. The following are some of these key strategies:
- Culture of Innovation: Foster an environment where employees feel free to share ideas without fear of reprisal.
- Investment and Financing: Allocate resources for the development of innovation projects.
- Multidisciplinary teams: Form teams with people from different departments and levels of experience to encourage diversity of ideas.
- Rapid Prototyping: Implement methods such as agile design or Lean Startup to quickly test ideas and adapt.
- Metrics and KPIs: Establish performance indicators to assess the impact of innovation initiatives.
- Innovation Governance: Establish processes and policies that regulate how decisions are made in innovation projects.
- Lifelong learning: Encourage learning and constant updating in innovation tools and methods.
Al combine a clear understanding of the different types of innovation with a sound internal managementorganisations have a increased likelihood of success in their efforts to innovate.
Practical Examples of the Innovation Ambition Matrix
To better understand the Innovation Ambition Matrix, here are some of the key questions to consider practical examples at each of the quadrants:
- Incremental Innovation: A software company that releases periodic updates to fix bugs and improve product performance. Here, the risk is low and the improvements are small but cumulative.
- Radical Innovation: Apple's introduction of the iPhone in 2007. This product changed the way we interact with technology and revolutionised the mobile phone market. The risk was high, but the impact was monumental.
- Process Innovation: Toyota and its "Just In Time" production system. This change in the production process significantly reduced costs and increased efficiency, although it was not an innovation in the product itself.
- Business Model Innovation: Netflix and its transition from a DVD-by-mail rental service to an online streaming platform. This change in business model not only affected its own performance but also changed the way we consume content.
How do these examples connect to internal innovation management?
- Incremental Innovation: It could be managed by an internal team dedicated to improving the existing product, with a relatively small budget and short lead time to show results.
- Radical Innovation: It requires a strong R&D team, significant funding, and a culture that allows failure as part of the learning process.
- Process Innovation: Generally driven by the operations and continuous improvement teams, in collaboration with line employees who know the day-to-day details of production or service delivery.
- Business Model Innovation: It often requires the involvement of senior management, as it may involve significant changes in the way the company operates and generates revenues.
I hope these examples help to clarify how the Innovation Ambition Matrix works and how it can be applied in different business contexts.
Artificial Intelligence applied to the Matrix
The use of artificial intelligence can be a valuable tool for companies and teams looking to apply the Innovation Ambition Matrix in various forms:
- Idea Generation:
- Incremental Innovation: Artificial intelligence can help generate ideas for minor improvements to existing products or services.
- Radical Innovation: It can offer cutting-edge ideas that could transform a market or industry.
- Data Analysis:
The language model can process large amounts of text data to identify opportunities or trends that might fit into different quadrants of the matrix. - Team building:
It can be used to create educational materials or guides to help team members understand the different types of innovation and how they fit into the matrix. - Risk Assessment:
Artificial intelligence could help in the preparation of risk analyses for different types of innovation, offering insights that may not have been considered. - Strategy Development:
It could assist in the elaboration of strategic innovation plans, generating potential scenarios and recommending courses of action. - Dialogue Facilitation:
In meetings, a chatbot could act as a neutral facilitator, proposing questions and discussion topics to help explore different areas of the matrix. - Monitoring and Updating:
It could be programmed to track the progress of innovation initiatives and remind teams of key steps or deadlines. - Multilingual support:
For global companies, the ability of artificial intelligence to understand and generate text in multiple languages could be useful for implementing innovation strategies in different markets.
By using artificial intelligence effectively, companies can accelerate and improve its innovation decision-making process, ensuring that all possibilities are properly considered and evaluated.
CASE STUDY
Juan and his Startup "EcoCharge".
Company and Sector: EcoCharge - Sustainable Technology
Context: Juan is the founder of "EcoCharge", a startup focused on solar-powered electric vehicle charging stations. He joins an accelerator programme to take his idea to the next level.
Problem: Despite having a solid business idea, Juan realises that growth has stalled. He is not sure how to scale his business and make it more innovative.
Application of the Innovation Ambition Matrix
During the acceleration programme, Juan comes across the concept of the Innovation Ambition Matrix and decides to apply it to "EcoCharge".
- Incremental Innovation: First, it focuses on incremental improvements, such as upgrading the power management software and making minor adjustments to the design of the charging stations.
- Adjacency Innovation: Next, it considers entering new markets, such as energy storage systems for households.
- Radical Innovation: Finally, it envisions developing a network of autonomous charging stations that can travel to high-demand areas using AI.
Implementation
For Incremental Innovation, an internal team is formed to optimise the performance and efficiency of existing charging stations.
- For the Adjacency InnovationThe company has entered into strategic alliances with energy storage companies.
- For the Radical InnovationJuan decides to apply for a government grant and seeks investors willing to bet on his long-term vision.
Results
- The incremental improvements result in a increase of 20% in the efficiency of the stations, attracting more customers.
- The entry into the domestic energy storage market adds an additional new source of incomediversifying its business.
- Although still under development, the idea of radical innovation generates a great deal of media interestpositioning EcoCharge as a leading innovator.
Success
By applying the Innovation Ambition Matrix, Juan manages to obtain additional investments y subsidies that accelerate the growth of "EcoCharge". The acceleration programme culminates with a financing round Juan is preparing to take "EcoCharge" to a global scale.
In a nutshellthe Innovation Ambition Matrix not only gave John an opportunity to roadmap for innovation but also provided a structure to balance risk and maximise return, taking "EcoCharge" to the next level.
QUIZZES
APPLY THIS TIP TO YOUR PROJECT
- 💻 PRACTICE with an expert in the next practical webinar.
- 🔎 CONSULT more related TIPs with this same theme.
- 📖 AMPLIA your knowledge by downloading this EBOOK.
THINK ABOUT YOU
- 🚀 IMPULSA your company in the next acceleration programme, ¡book your place now!.
- 🥁 PRACTICE with your project in this practical webinar, ¡apply for your place!.
- 🌐 CONTACT with other entrepreneurs and companies, ¡register and take part in the next Networking!
THINK ABOUT HELPING OTHERS
- 🤝COLLABORATE as a volunteer: expert, mentor, inverter, awarding, Spreading the word, challenging, innovating, creating a TIP...
- 💬 RECOMMENDS this programme to reach out to more entrepreneurs by Google.
- 👉 SHARE your learning!
- 📲 SEND this TIP 👇








