Social innovation
Accelerate your business with these expert tips on "Social Innovation".
Analyse and discover this TIP!
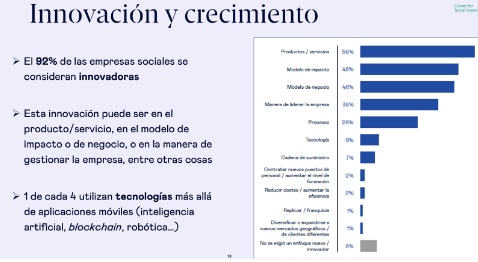
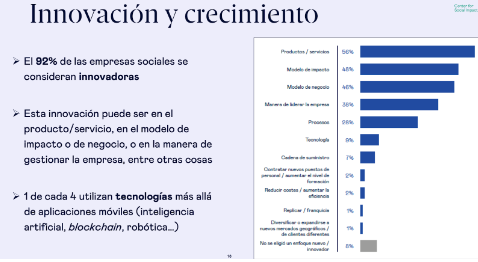
The Social innovation focuses on the creating innovative solutions for addressing social challenges o improve people's quality of life. This may include projects related to education, health, sustainability, social inclusion, among others.
The social innovation is a multidisciplinary and collaborative approach which seeks to create innovative solutions to solve complex social problems o improve the quality of life of individuals and communities. It differs from other types of innovation in that its main objective is not economic profitAlthough this may be a positive side result, if not the positive social impact.
Los negocios inclusivos buscan activamente la participación de personas en riesgo de exclusión, generando valor económico, social y ambiental. Características clave incluyen la participación activa, sostenibilidad, creación de valor social y ambiental, enfoque comunitario e innovación social.
Tabla de contenidos
Emprender con Sostenibilidad
Definir un propósito sostenible antes de iniciar es crucial. Integrar prácticas éticas desde el principio, innovar constantemente en impacto social y ambiental, y construir relaciones sólidas con comunidades locales son pasos fundamentales. Los beneficios incluyen seguridad de abastecimiento, menores costos de transacción y acceso a financiamiento y redes locales.
Innovación Social
La innovación social es esencial en empresas sostenibles. Se distingue de la innovación económica, tecnológica y estratégica. Su definición abarca soluciones nuevas a problemas sociales, siendo beneficiosa para la sociedad y con un doble objetivo de misión social y creación de valor económico y social. Se desarrolla en tres etapas: gestación, implementación y cambio sistémico.
Qué es y que no es la innovación social
La innovación social no debe confundirse con emprendimiento social ni economía social. Diversas definiciones destacan su naturaleza de proceso que busca mejorar el bienestar humano y resolver demandas sociales, con cuatro elementos básicos: identificación de necesidades, desarrollo de soluciones, evaluación de eficacia y ampliación de innovaciones eficaces.
Etapas del proceso de innovación social
Identificadas tres etapas: gestación, implementación y generalización y cambio sistémico. Otras propuestas consideran seis etapas, desde el surgimiento de la idea hasta la implementación, sostenibilidad y cambio sistémico. Evaluar la ampliación y difusión de ideas y aprender y evolucionar son etapas finales cruciales.
Experiencias y Ejemplos de Innovación Social
La UE destaca ejemplos como inclusión social, migración, regeneración urbana, economía social, microfinanzas y más. Empresas, entidades financieras y Administraciones públicas impulsan la innovación social. Ejemplos prácticos incluyen proyectos de emprendimiento social, financiamiento ético, programas de Administraciones públicas y colaboraciones público-privadas para mejorar condiciones de vida en países en desarrollo.
Key Components of Social Innovation:
- Creating Innovative Solutions: Social innovation is not simply about doing something "new", but about doing something "better" in the social context. This might involve developing new technologies or using existing technologies in novel ways to address social problems.
- Addressing Social Challenges: The focus is on solving problems that affect society as a whole or specific communities within it. These problems can range from poverty and inequality to climate change and health care.
- Improving the Quality of Life: It is not only about solving a problem, but also about improving the quality of life of the people affected. For example, an app that facilitates access to health services in rural areas not only solves the problem of access, but also improves the quality of life by making health care more accessible.
Areas of Application:
- Education: Development of accessible online educational platforms, mentoring programmes for disadvantaged students, or curricula that encourage critical thinking and inclusion.
- Health: Solutions ranging from mobile applications for chronic disease monitoring to community-based programmes to improve mental health.
- Sustainability: Projects that address sustainability from an innovative perspective, such as community-based renewable energy systems or recycling and circular economy programmes.
- Social Inclusion: Programmes that seek to empower marginalised groups, such as employment platforms for people with disabilities or projects that promote the inclusion of ethnic and cultural minorities.
In short, social innovation is a field that combines creativity, collaboration and understanding of social dynamics to develop solutions that have a positive and lasting impact on society.
Practical examples of social entrepreneurship and innovation, showing different ways of tackling community, social and environmental problems:
- Who Gives A Crap
- Sector: Personal Hygiene / Toilet Paper
- Social Impact: 50% of the proceeds go to build toilets in disadvantaged communities.
- Business Model: Online sales of eco-friendly toilet paper.
- Innovation: Use of sustainable materials such as bamboo and recycled paper.
- Ecolife Recycling
- Sector: Recycling
- Social Impact: Recycling plastics to reduce pollution.
- Business Model: Sale of recycled products and recycling education.
- Innovation: Development of an environmentally friendly method for recycling plastics.
- Freewheel Mobility
- Sector: Transport and Mobility
- Social Impact: They offer transport solutions for people with reduced mobility.
- Business Model: Sale and adaptation of vehicles.
- Innovation: Design of personalised transport systems for people with special needs.
- Lava Mae
- Sector: Health and Hygiene
- Social Impact: They offer mobile showers for homeless people.
- Business Model: Funding through donations and partnerships.
- Innovation: Conversion of buses into mobile toilet facilities.
- Solar Sister
- Sector: Energy
- Social Impact: Empowering women in Africa by selling solar energy solutions.
- Business Model: Direct sales of solar energy products.
- Innovation: Network of women entrepreneurs distributing solar technology in rural communities.
- Kiva
- Sector: Microfinance
- Social Impact: They offer microcredits to entrepreneurs in developing countries.
- Business Model: Online platform for peer-to-peer lending.
- Innovation: Using technology to connect lenders with small entrepreneurs.
- Teach for All
- Sector: Education
- Social Impact: They seek to reduce educational inequality by training teachers in disadvantaged areas.
- Business Model: Funded by donations and grants.
- Innovation: Collaborative educational model at international level.
Each of these examples shows how social entrepreneurship and innovation can address a variety of problems with sustainable and scalable business models.
Artificial intelligence can offer multiple forms of assistance to entrepreneurs interested in social innovation.
Here are some concrete ways in which this could be useful:
- Idea Generation:
Artificial intelligence can help brainstorming of business ideas that meet social and environmental objectives, suggesting areas where social innovation is needed and types of solutions that could be effective. - Concept Validation:
It can help analyse the feasibility of a business idea by studying similar business models, market strategies and potential challenges. - Strategic Planning:
It can assist in the development of a business plan, suggesting key points to be addressed, from stakeholder identification to financing strategies. - Orientation in Financing:
Artificial intelligence can provide information on the various forms of funding available to social entrepreneurs, from grants and impact loans to crowdfunding. - Skills Development:
It can provide educational resources to improve relevant skills, such as leadership, negotiation, and social skills that are vital to the success of any social enterprise. - Communication and Marketing:
It can assist in creating marketing content that highlights the company's social impact, which could attract more customers and partners interested in social causes. - Impact Analysis:
It can provide guidance on how to measure the social impact of the enterprise, which is crucial for any venture in the field of social innovation. - Legal and Regulatory Advice:
While it cannot replace professional legal advice, artificial intelligence can provide an overview of legal and regulatory considerations specific to social enterprises. - Connection to Resources:
It can point to useful resources such as articles, books, online courses and organisations that can help at different stages of social entrepreneurship. - Emotional Support:
Entrepreneurship can be a lonely and stressful journey; having a "partner" with whom to discuss ideas and concerns could be invaluable, even if this support comes from an artificial intelligence.
The key is how this tool is used. With the right guidance, artificial intelligence can be a valuable resource for any social entrepreneur.
CASE STUDY: Maria and ReciPlastic
Sector: Sustainable technology
Context: Maria is an environmental engineer who participated in mentorDay's accelerator programme. Before the programme, she had a basic but powerful idea: to reduce the use of single-use plastics by creating an efficient recycling system that transforms these plastics into filament for 3D printers. His company, "ReciPlastic", aims to be a social business that not only generates revenue but also has a positive social and environmental impact.
Challenges:
- Lack of financial resources for start-up.
- Lack of a defined market strategy.
- Need to validate the technological and social feasibility of the project.
How mentorDay helped:
- Specialised Guidance: Maria was mentored by experts in social business and sustainability.
- Business Model Validation: The programme helped Maria to conduct market research and validate the need for her solution.
- Access to Finance: She was introduced to different funding opportunities and helped to prepare a pitch to investors.
Applied Social Innovation:
- Circular Recycling System: ReciPlastic developed a method of collecting single-use plastics and transforming them into usable material.
- Community Participation: The model included the participation of the local community, which could earn points redeemable for every kilo of plastic recycled.
- Environmental Education: Through workshops and educational programmes, ReciPlastic educated the community about the importance of recycling and sustainability.
- Transparency and Traceability: They implemented a blockchain system to ensure the traceability of the recycled plastic life cycle.
Results:
- Social and Environmental Impact: In its first year, ReciPlastic managed to recycle more than 50 tonnes of plastic and educate more than 5,000 people on sustainable practices.
- Financial sustainability: Thanks to partnerships with local organisations and grants, ReciPlastic achieved financial self-sufficiency.
- Scalability: The model is being prepared for expansion to other cities, and partnerships with international organisations have already been established.
Lessons learnt:
- The importance of validating the idea before scaling up.
- The need to involve the community in the solution.
- The impact of specialised training and mentoring on project acceleration.
This case shows how, with the adequate support and the application of social innovationan entrepreneur can transform an idea into a sustainable, high-impact social business.
QUIZZES
APPLY THIS TIP TO YOUR PROJECT
- 💻 PRACTICE with an expert in the next practical webinar.
- 🔎 CONSULT more related TIPs with this same theme.
- 📖 AMPLIA your knowledge by downloading this EBOOK.
THINK ABOUT YOU
- 🚀 IMPULSA your company in the next acceleration programme, ¡book your place now!.
- 🥁 PRACTICE with your project in this practical webinar, ¡apply for your place!.
- 🌐 CONTACT with other entrepreneurs and companies, ¡register and take part in the next Networking!
THINK ABOUT HELPING OTHERS
- 🤝COLLABORATE as a volunteer: expert, mentor, inverter, awarding, Spreading the word, challenging, innovating, creating a TIP...
- 💬 RECOMMENDS this programme to reach out to more entrepreneurs by Google.
- 👉 SHARE your learning!
- 📲 SEND this TIP 👇
Rate this TIP!
Click on the stars to rate
Rating "0" - Average " - Average0"
No votes yet, be the first to vote!
We are sorry you did not find it useful.
Help us improve this TIP!
Leave us a comment and tell us how you would improve this TIP