INNOVATIVE BUSINESS MODELS
Accelerate your business with these tips "Innovative business models". Analyse and discover this TIP!
There are a number of innovative business models that have emerged in recent years, some of the most prominent of which include
- Subscription model: Companies using this model offer their products or services on a regular subscription basis, which allows for greater loyalty and a clearer forecast of recurring revenue. An example of this model is the music streaming service Spotify.
- Freemium model: This model consists of offering a free basic service, but also a paid premium version that includes more functionalities and additional features. An example of a company using this model is LinkedIn, which offers a free basic service and a paid premium version.
- Collaborative economy model: This model is based on the exchange of goods or services between individuals, without the need for a traditional intermediary company. An example of a company that uses this model is Airbnb, which allows individuals to offer their homes as temporary accommodation.
- Crowdsourcing model: This model consists of outsourcing tasks or projects to a community of people via the internet, thus allowing for greater efficiency and cost reduction. An example of a company using this model is the graphic design platform 99designs.
- Crowdselling model: This model is based on selling products through social networks or online communities, using the power of user recommendations to increase sales. An example of a company using this model is the cosmetics company Younique.
- Marketplace model: This model is based on the creation of an online space that connects buyers and sellers, allowing for greater transparency and efficiency in the transaction. An example of a company using this model is Amazon, which allows private sellers to offer their products through its platform.
These are just a few examples of innovative business models that have emerged in recent years that have revolutionised the way companies generate revenue and create value for their customers.
What characterises an innovative business model?
An innovative business model is characterised by differentiating elements in its value proposition, in the way it generates revenue, in its relationship with customers and in the way it uses its key resources and activities. In addition, it focuses on identifying and satisfying unmet needs in the market, and in creating new ways of generating value for customers and the company. Therefore, the innovation is a key element in these models, as they seek to create disruptive solutions that change the way things are done and create new business opportunities.
What is one of the advantages of using an innovative business model?
One of the advantages of using an innovative business model is that it can enable a company to differentiate itself from its competitors and create a sustainable competitive advantage in the market. In addition, it can help the company to identify new business opportunities and adapt quickly to market changes. It can also increase customer satisfaction by offering innovative solutions that meet their needs more effectively.
What is disruption in the context of innovative business models?
In the context of innovative business models, disruption refers to the ability of a company or business model to radically transform an existing market or industry. It is a disruptive innovation that alters the rules of the game and changes the way things are done in a given industry. Disruption often involves the introduction of new products, technologies or business models that are more efficient, more convenient or more accessible to consumers.
It can also involve cutting out intermediaries or creating new markets. Disruption can be both a threat and an opportunity for existing businesses, and many companies are constantly looking to innovate and adopt new business models to keep up with market changes.
One of the tasks that any professional with business responsibilities must address periodically, whether they are CEO of a Fortune 100 company, budding entrepreneur, CEO of a newly created startup or Managing Director of an SME, is to question their business model, i.e. how they intend to operate and make money (or social value, in the case of an NGO). This involves not only analysing the current one but also considering new models that provide more value.
To do this, there is nothing better than understanding where we come from and, above all, which are the most successful models of late, a basis on which to draw inspiration and question one's own model. Business models at the beginning of the 20th century were quite simple: you made something / provided a service and sold it live. Gradually, however, new alternative ways of generating income were developed.
TWO OF THOSE THAT HAD THE GREATEST IMPACT ON THE INDUSTRY WERE:
- Gillette: To explain the implications and previous steps of this business model would be lengthy (it is often used as a case study in Master's courses), so let's summarise: King Gillet felt that, if he could offer good razors at a very competitive price, customers would be happy to pay for the blades (which would require periodic replacement).
- Xerox: When in 1959 Xerox introduced its 914 model, with features far beyond those of the photocopiers sold at the time (and much more expensive), it decided to innovate its business model: Instead of selling each machine in the traditional way, it would rent them by charging an additional 0.04$ for each copy from 2000 copies per month.
In recent times there has been a certain amount of concern about this, given the global pressure to increase competitiveness and productivity, which, together with the advent of the Internet and the collaborative web, has led to a whole range of alternative business models. Below we will look at some of the most interesting ones (obviously they are not pure models, and in many cases some have traces of others).
2 MODELS (0 VARIOUS BUSINESSES)
These are business models in which there are at least 2 (although there may be more) interdependent groups of customers (sides). This type of business model stems from the fact that one side only benefits if the other side is present, and therefore the main objective of the company is to facilitate the interaction between them, acting as an intermediary and maximising the network effect.
The key premise for this approach to succeed is that it must attract and create value to both sides equally. If it only offers real value to one of the two sides, the other quickly diminishes and ceases to have value in its own right. This type of business model stems from the fact that one side only benefits if the other side is present, and therefore the main objective of the company is to facilitate the interaction between them, acting as an intermediary and maximising the network effect.
The key premise for this approach to succeed is that it must attract and create value on both sides equally. If it only offers real value to one of the two sides, the other quickly decreases and becomes worthless in its own right. For this purpose, usually one side is subsidised, i.e. the service you receive is heavily discounted (or free) at the expense of the non-subsidised side.
A good example of this type of business model and how a business model can make a sector rethink its dogmas is the Metro newspaper (and all its derivatives): There is a subsidised side (the general public) that receives a free product on a daily basis. The subsidising side subsidises the arurc,ates who consider^ the model as long as there is a sufficiently large base of members on the other side (the general public).
Other examples of two-sided business models include Google (connecting advertisers with users of their products), console manufacturers such as Nintendo Wii or PS3 (connecting game developers with customers), credit card manufacturers (connecting shoppers with retailers) or even the press.
Although it is not a "pure" case of a multi-sided business model, I found the case of the Safaricom operator very interesting, described beautifully in the indispensable "Gurusblog. It is a Kenyan operator that, in addition to operating as such, detected the need for agile banking services for a large part of rural Africa... so, taking advantage of its infrastructure and mobile phones, it invented a system for people to pay, collect and send money.
An example that perfectly illustrates these markets (specific case of a two-sided market) can be found in our youth and the hours spent in a discotheque: One side of the market (girls, subsidised side) had free access to the discotheque which was mainly taken over by the other side (the boys who paid admission, hoping to find enough customers from the other "side"), as well as by an additional source of income (the drinks).
LONG TAIL
Its name was coined by Chris Anderson in his Wired article, and is based on the fact that in certain businesses there are finite resources that force the company/business to choose to sell only the products that are expected to have the best sales. The model is called "Long Tail" after the razor manufacturer Gillette. It is based on the presence of an attractive and very cheap initial offer that builds customer loyalty to the razor and subsequently encourages the customer to continue buying products or services.
It changes the obligation and complexity of selling new units every month only to having a recurring income in addition to the units sold... at the cost of taking an initial loss. In this type of business it is very common that the seller initially loses money with the customer, creating the profits with each subsequent purchase.
In addition to the previous example, telecommunications operators offer us another very didactic example: When we want to change our mobile phone, we go to an operator, which makes us a very attractive offer (bait, assuming the total or a large part of the cost of the mobile phone) in exchange for a contract of permanence of 1 or several years (bait), which is where the real benefits are generated, derived from having a tied customer.
CLOUD AND SAAS (SOFTWARE-AS-A-SERVICE)
Although technologically they are not at all the same, at the level of business approach they are very similar: The main value proposition is based on the transformation of a product into a service and of a fixed cost into a variable one. The customer does not have to buy an expensive software (product, edge cost), which must then be installed on additional hardware and pay for a subscription and support (variable, periodic), but pays to receive a service on a monthly (or yearly) basis.
One of the best known examples is Salesforce: this is CRM (customer relationship management) software where the user only pays for access to the software (number of users) and for which modules they need to use (functionality), rather than paying for an expensive CRM to buy, install and maintain. Another great example of how a SaaS model can turn a market around is Business Intelligence: companies like LiteBi have been able to make complete BI software available to any company, regardless of size.
FREEMIUM
This is a particularisation of the two-sided business model, where one of the two sides continuously receives a completely free service/product. For this to happen, non-paying customers must be subsidised by another customer base or even by another side of the business model.
The most popular option; and the one that most Internet services nowadays rely on is to offer a basic (free) service to the majority of users while a small number of them pay a fee to get a more comprehensive (premium) service. This is only possible if the services are based on a platform that aggregates costs and makes scaling very cheap (given that the ratios of paying users vs. free users are usually around 1-2%).
That said, there are a number of additional ways to subsidise the free user base, which may involve the use of advertising (although this is often a poor choice, as it leaves the only revenue stream in the hands of a third party) or finding other revenue channels (bands such as Radiohead have experimented with this concept, releasing their songs for free and making a profit on concerts and merchandising).
For more information on this model, I recommend Chris Anderson's excellent post "Free! Iy-, $0.00 Is the Future of Business".
CO-CREATION AND CROWDSOURCING
Crowdsourcing is a different approach to value creation, based on involving a large crowd in solving a problem or providing a service in exchange for a reward, which we have discussed several times.
THERE ARE MANY WAYS TO USE CROWDSOURCING AS THE BASIS OF A BUSINESS MODEL, BUT IN MY OPINION THE MOST INTERESTING ONES ARE:
- Pure communities (from Wikipedia or iStockPhoto to Threadless), where the crowd performs tasks typically done by internal staff and whose business model has been built on this approach.
- Contests/Challenges is really a particularisation of a two-sided marketplace with a few drops of crowdsourcing: A number of users (business side) propose a problem to the masses, and the winner of the contest (crowd side) gets paid when the contest is solved. A classic example is design auctions such as 12Designer.
- Ideagoras: Places where companies can "rent" a crowd to solve scientific or technological problems in exchange for a reward, or obtain very valuable feedback from customers or users (it is a materialisation of Open Innovation). The most prestigious ones are Worthldea (with a presence in Spain and some great ideas), Innocentive and NineSigma.
In this type of initiative, revenues usually arise from capturing a share of the value of transactions.
SOME OF THE MOST IMPORTANT ASPECTS:
- For the initiative to succeed, the market must be large enough (the crowd).
- The problem or need must be well described and designed in a way that is understandable.
- Acquiring new members of the crowd is key, so marketing takes on a vital role, as well as encouraging existing members to stay involved (community management).
- Adequate reward (not only in terms of money) should be established.
- Define a correct cash flow: If it is a contest/challenge type business model, it is important that the "enterprise" users pay up front, so that the company has enough cash until the contest is resolved.
There are many other types of business models (Auctions, Low-cost, Affiliates, Add-on, mobile applications, Services/Consulting, Distribution, Franchises, Contests, Subscription, sale of virtual products...) that if you find interesting I will discuss in future articles. In the meantime, I recommend you to see the list of business models that Javier Martin (Loogb) explains very clearly on his website.
Likewise, if you want to study the business models of successful companies (from Lego to Zara to Tata), I recommend you consult The Business Model Database ..... The business model of Somali pirates has even been analysed. Business models are constantly evolving.
Sometimes it is because technologies are changing and it is necessary to adapt the way in which products or services are offered to customers. At other times, the reason is that customers' preferences and needs are changing, so companies have to keep up with the changing needs of their customers. innovating and adapting to a constantly evolving market.
In any case, the business models The business models we know today may be different in the future, they may continue to be successful as they are today, and we probably do not yet know what new business models will come in the future.
Crowdfunding Model
This type of business model is based on a collaborative model between individuals and professionals. Its modus operandi is based on the crowdfunding or collective cooperation carried out by the users of the platform, who collaborate by contributing financial resources. The objective is financing ideas, businesses or projects that can be of great value to society.
These contributions are generally made through donations, shares, loans or royalties. One of the main advantages is that many of these projects that seek funding often go viral, so if the necessary funding is obtained, it is easier to have a more loyal group of customers. However, it should be borne in mind that the The risk of announcing a project that is not yet underway means that it could be copied by other companies.
One example of success is the case of the Pebble smartwatches whose first campaign had a target of 100,000 dollars. However, it was such a success that it reached 10 million dollars.
This allowed them to launch their flagship product before Apple Watch entered the market, after which it was acquired by FitBit.
Blockchain model
The digital transformation is a fact that sooner or later companies need to adapt to, but it is much better if the process is streamlined, and furthermore, without having to resort to intermediaries. A novel business model that is still in its infancy. The new system will be fully developed and will serve to streamline a multitude of processes: on Blockchain model. This model is advantageous because it implies a low cost for users by reducing intermediaries.
However, the cost of implementation can be high and the loss of private keys can cause a problem in information retrieval. Blockchain technology is very useful in a multitude of cases, such as for example example: in auditing, supply chain management, counterfeit detection or cybersecurity, among other areas.
Multilateral platform model
Some of the best known and most successful companies of recent times have implemented this innovative model, which consists of acting as an intermediary, bringing together two or more groups seeking an interest: what is known as a "matchmaking". matching supply and demand.
In return, the platform generates revenue through advertising or commissions. Thanks to this type of platform, there is a benefit for sellers or service providers, and for users who are looking for an advantage, a financial saving or an incentive.
In addition, the platform does not need to make a high investment in assets. However, if there are no transactions, no revenue will be generated, so it is necessary to incentivise trading and improve the visibility of the platform. Some of the best-known companies that have achieved success through this system include Wallapop business model o Google model.
Long Tail Model
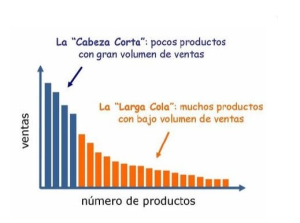
Also known as long-tailed modelThis type of business is based on a mathematical principle that has proven to be very successful: the Pareto Principle. This principle is based on the fact that 20% of products will generate 80% of sales. It will therefore rely on selling fewer units of a large number of products.
Some advantages of this business model are that there is less competition and it is possible to creating customised products that target more specific customer groupsThis will lead to greater satisfaction. However, it requires a sufficiently large supply and demand for good profitability. eBay o Amazon are an example of large shops that sell a multitude of products of all kinds, but in limited quantities.
Dropshipping
The Dropshipping business modelis the one that many companies prefer when they do not have the capacity to invest a large amount of money in machinery, logistics network, or warehousing. In this case, the company acts as an intermediary, but does not physically own the products it sells to the customerInstead, the shipment will be made by a third party, who will deliver the product directly to the customer on behalf of the main company.
The best thing about this business model is that you do not need to have a warehouse or invest a large sum of money upfront, however it would not be possible to offer a customisation of the products and therefore a lower quality of customer service. Ebay or the Shopify model are two of the platforms that allow this type of business to be set up.
Subscription boxes
The subscription box business model is one of the most recent and innovative we can find. Through this business model, which is integrated with the subscription model, the customer receives a series of products of interest to him on a regular basis.
The idea is that the value of the products is higher in relation to the subscription priceThe customer perceives that he or she is buying something of great value. The problem with this business model is that customers cannot choose the products in the box, so not everyone will be satisfied and it may even lead to unsubscribes.
Some examples of companies that have successfully implemented this type of business is the beauty company Birchbox model which offers beauty care products, Degustabox to receive food products or Nonabox to receive baby products.
Collaborative economy model

The exchange of goods and services between private individuals has become a profitable business model, convenient and with interesting benefits for the people who offer their goods or services as well as for the people who demand them. A business that is constantly evolving and encourages the responsible use and consumption of goods and services.
They can offer everything from house rentals, to carpooling, second-hand goods and even catering services among many other options. The most attractive aspect of this business model is the wide range of niches available on the market, as well as the savings for customers.
Some examples of companies participating in this collaborative consumption are the model from Airbnb with the offer of private accommodation for travellers, or the Blablacar business model and its carpooling service to reduce the cost of travel.
Cloud Computing
This business model has emerged thanks to the increasingly popularised use of digitised information (see digital business model). From private individuals to large companies, the digital world is a reality that requires advanced tools for a more efficient management of all documentation in digital format that moves every day in this field.
Applications created to manage information in the cloud have boomed spectacularly as they allow large amounts of data to be stored, updated, sent and even synchronised quickly and for very affordable fees.
However, it requires absolute dependence on the network, with all the irregularities and technical problems that this may entail at some point. Dropbox o Google Drive are examples of companies that have branded this file storage and management system, with solutions adapted to individuals and companies, limited free storage and a multitude of functions.
Subscription model
A revolutionary model when it first came into use and now one of the best known models. More and more companies are opting for the subscription form in order to maintain some economic security for the implement a subscription system for access to its services.
In this way, for a regular payment, customers have the opportunity to unlimited access to all company functions and offers. This model allows the creation of a stable customer base and the company receives recurring revenues.
But it also means that the customer no longer appreciates the value of what he is buying for the price he is paying, and decides to cancel his subscription. Canvas Netflix o Hootsuite are some of the best known examples of successful implementation of the subscription model.
Freemium model
A newer version of the subscription model is the Freemium model. In this case, customers have the option of being able to try the service and even use it for free. However, the business adapts to customers who want to enjoy exclusive functions, and therefore integrates a subscription model for unlimited access to all product or service benefits.
However, this model is very profitable, there needs to be a sufficient quota of customersThe Commission has also decided that the customer should choose to subscribe to unrestricted access, so that it is profitable to maintain the share of customers who prefer to use basic access. The music application with the Spotify canvas model or the Deezer model or the podcast application Ivoox are an example of companies that offer a basic service with the option to upgrade to a more advanced service for a fee.
Chatbot business model
A chatbot is another of the most innovative ideas that you can implement as a business model in your company. But what is this tool? A chatbot is a software that can run on websites or social networks and that can chat with users 24 hours a day automatically resolving doubts or solving simple questions.
The best thing about this business model is that it allows you to get leads, i.e. new customers or followers that increase your company's database, making them very useful for publicising new businesses or launching marketing campaigns. However, it should be noted that is still an automatic answering machine, so it will not always give a satisfactory 100% response.
Some successful examples of chatbots that have improved the customer experience include Madison Reeda chatbot from an American brand that helps users find their perfect gentleman's shade.
The mattress company Casper is also committed to this innovative idea by creating a chatbot that accompanies people who suffer from insomnia.
Gamification business model
The gamification business model is a relatively recent concept that has, however, greatly improved the customer experience, which is why more and more companies are implementing it in their businesses.
The idea is to enhance a brand's value proposition by turning customers into "players".The aim of the project is to create a new service, i.e. by applying techniques related to the world of videogames to motivate users to use a certain service.
This type of strategy improves customer loyalty at the same time that it encourages and motivates them to continue consuming a company's services or products through a rewards programme, ranking, promotions...
An example of gamification is the Duolingo business modelThe free language learning website, which allows you to earn points and move up in a ranking in which you compete with other users. By reaching certain challenges you will get a certificate and you will go up levels.
Flash Sales business model
The flash business model salts is based on launch, for a short period of time, very attractive offers that aim to generate a sense of urgency among customers.. Thanks to the collaboration with a multitude of companies in various niches, these platforms manage to offer incredible promotions with very limited stock, which the customer will only have available for a few days or even a few hours.
The best thing about this type of business is that it is able to achieve a good volume of sales in a very short space of time and allows companies to dispose of accumulated stock. However, it requires a rigorous study of profit margins in order to avoid incurring losses.
Some of the most successful companies that have made flash sales their business model include Privalia o Groupaliawhich offer products and services at very low prices in a short period of time from a wide variety of brands.
E-learning business model
Recently it has become very fashionable to share knowledge on the internet with other users. This e-learning business model is based on the creation of a platform from which digital products are offered, also known as infoproduct business model.
The aim is that clients can enjoy knowledge that will broaden their training or simply help them to develop other skills, online. This business model allows for direct sales as access to online courses, webinars, guides, or tools is achieved by a one-off payment giving access to the full content.
They usually have a large number of followers and allow for passive income. However, plagiarism is one of the risks of this business model.
E-learning platforms such as the Udemy business model o Coursera are an example of media that are betting on the e-learning business to offer paid online courses to their users. Some of them are even endorsed by prestigious schools or universities, which increases the value of their services.
Comparator business model
The comparator business model is another new and successful venture born out of the need for users to compare all the offers available on the market to find the one that best suits their needs, budget or preferences. Thus, by using a single website, customers not only get an overview of the entire offer available to them, but also get direct access to these websites or an overview of all features and prices.
One of the advantages of this type of business model is that it hardly requires a large initial investment, and if customers decide to contract any of the services offered by the platform, they can obtain succulent fees. On the other hand, however, a complex structure is required to ensure up-to-date results in line with the client's criteria.
WE CAN FIND COMPARATORS FOR DIFFERENT CATEGORIES:
Some of the best-known online comparison sites include Idealospecialised in the search of products from the most famous marketplaces such as Amazon or eBay, or Preciosmundi to find the best prices in different supermarkets around the world.
APPLY THIS TIP TO YOUR PROJECT
QUIZ
- 💻 PRACTICE with an expert in the next practical webinar.
- 🔎 CONSULT more related TIPs with this same theme.
- 📖 AMPLIA your knowledge by downloading this EBOOK.
THINK ABOUT YOU
- 🚀 IMPULSA your company in the next acceleration programme, ¡book your place now!
- 🥁 PRACTICE with your project in this practical webinar, ¡apply for your place!.
- 🌐 CONTACT with other entrepreneurs and companies, ¡register and take part in the next Networking!
THINK ABOUT HELPING OTHERS
- 🤝COLLABORATE as a volunteer: expert, mentor, inverter, awarding, Spreading the word, challenging, innovating, creating a TIP...
- 💬 RECOMMENDS this programme to reach out to more entrepreneurs by Google.
- 👉 SHARE your learning!
- 📲 SEND this TIP 👇
Rate this TIP!
Click on the stars to rate
Rating "3" - Average " - Average4.7"
No votes yet, be the first to vote!
We are sorry you did not find it useful.
Help us improve this TIP!
Leave us a comment and tell us how you would improve this TIP










