OPERATING AND FINANCIAL LEVERAGE
Accelerate your business with these expert tips "Operational and financial leverage". Analyse and discover this TIP!
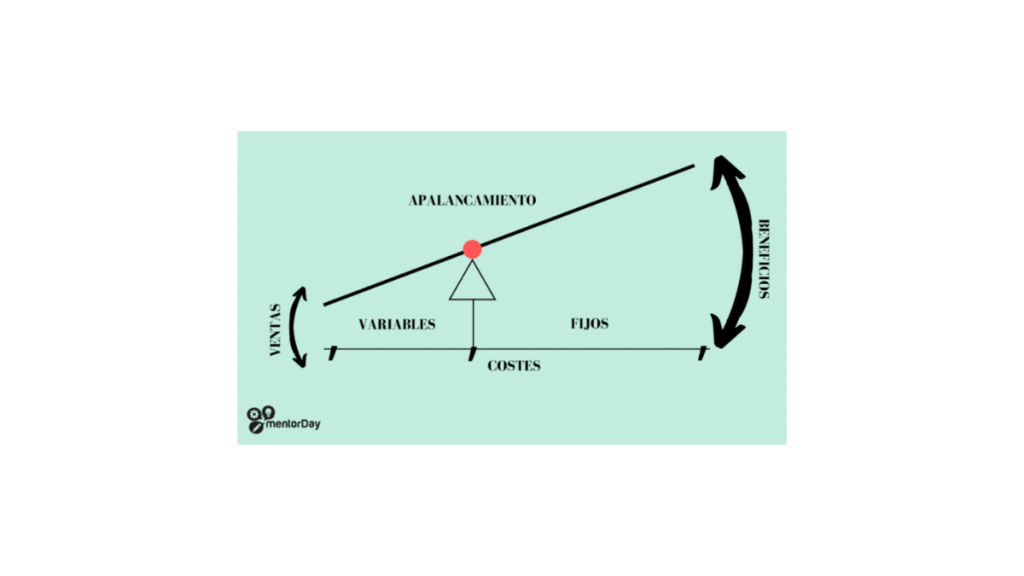
A company is said to be highly leveraged when it creates a cost structure with a high FIXED cost relative to the variable cost. This model has more economic risk and, also, more profit when sales increase. The startups (see+) scalable (+) investors are looking for, they have leveraged structures.
THERE ARE TWO TYPES OF OPERATIONAL AND FINANCIAL LEVERAGE
OPERATING LEVERAGE
Operating leverage consists of having a cost structure with more fixed costs than variable costs, in order to obtain a higher profitability per unit sold. Since as the quantity of goods produced increases, variable costs will increase at a slower rate and thus total costs (variable costs plus fixed costs) will increase at a slower rate as we increase the production of goods, resulting in a higher profit for each product sold. Operating leverage is the ratio of fixed costs to variable costs. It enables a business to reduce total production costs once it has produced more than a certain quantity. As the company's sales volume increases, each new sale contributes less to fixed costs and more to profitability. Therefore, operating leverage allows companies to enjoy higher gross margins (selling price minus variable costs) in every sale. We can know that a company has a high degree of operating leverage if the gross margin on its sales is very high. The more fixed costs are used, the higher the operating leverage.
RISKS OF OPERATIONAL LEVERAGE:
Operating leverage refers to the ratio of a company's fixed costs to its variable costs. It is important for start-ups because it can affect profitability and the company's ability to cope with fluctuations in revenue. A company with a high level of fixed costs will have higher operating leverage, meaning that a small change in revenue can have a large impact on profits. On the other hand, a company with a high level of variable costs will have lower operating leverage, meaning that the company is more able to adjust its costs as revenues change.
Operating leverage is calculated as the ratio of fixed costs to variable costs:
Operating Leverage = Fixed Costs / (Revenues - Variable Costs)
For example, if a company has fixed costs of $100,000 and variable costs of $50,000, and its revenues are $200,000, the operating leverage would be 1.33:1. It is important for a new company to consider its level of operating leverage when making costing and pricing decisions. A firm with a high level of fixed costs must be careful to adjust its prices to avoid losing profitability, while a firm with a high level of variable costs must consider ways to reduce its fixed costs to improve its ability to cope with fluctuations in revenues.
A high degree of operating leverage has a higher risk for the company. If it ends up selling fewer goods than expected and has to produce fewer products than it had predicted would be needed to break even, the total costs and losses from that activity will be higher than if it had lower operating leverage. To the business angels (+) They like companies that are more leveraged and therefore more risky for the entrepreneur.
FINANCIAL LEVERAGE
Financial leverage is the ratio of debt to equity of a company. In other words, refers to the amount of money a company has borrowed compared to the amount of money it has invested through equity or capital contributions. In the context of a new venture, leverage can be a useful tool to finance growth and expand the business. However, it can also carries risks, since, Increased debt can increase interest and debt payments, which can affect the profitability and solvency of the company.
Financial leverage is calculated as the ratio of debt to equity:
Financial Leverage = Debt / Equity Capital
For example, if a company has a debt of $100,000 and an equity of $50,000, the financial leverage would be 2:1. It is important to note that financial leverage can have a multiplier effect on a company's performance. If a company has a high level of leverage, even small variations in revenues can have a large impact on earnings. Therefore, it is important that, a company, be careful when using financial leverage and carefully consider the potential risks and benefits before making major financing decisions. Financial leverage refers to the effect that borrowing has on profitability. Small amounts of money can be used to make an investment that behaves like a much larger one. There are many large and stable companies that, in order to make the capital of their partners profitable, when they are going to make a new investment, they turn to bank financing to finance by minimising capital increases.
In project finance, a lot of external financing is used, increasing the financial risks. It is only of interest in the case of having a very constant assured income, which is complicated for entrepreneurial projects. For example, is what happens when buying options or warrants: By paying a small amount (the premium), the investor has the possibility of obtaining the same result as if he had bought or sold securities with a much larger market volume. While the option expires, the investor can earn a return on the money that he has not yet had to pay out to purchase the securities. Thus, an investment in warrants, can be much more profitable than the same investment in the underlying, if markets perform favourably to your position; But in return, the risk increases, and the possibility of losing the entire investment if the performance is not as expected.
More leverage means more profitability but also more risk!
Leverage can increase a company's profitability by allowing it to use debt to finance its operations instead of using its own capital. However, it also increases a company's risk because if its operations do not generate enough revenue to cover costs and interest on debt, it may be forced into bankruptcy. It is therefore important for companies to carefully assess the level of leverage they can manage without jeopardising their financial solvency. Leverage can increase a company's risk. The higher the level of leverage, the higher the amount of debt the company has in relation to its equity, which may increase the risk of default on debt repayment. If a company has a high level of leverage and its revenues decrease, it may not have enough cash to pay its debts, which can lead to bankruptcy. Therefore, the level of leverage must be carefully considered and managed to balance the financial benefits with the associated risks.
What level of leverage do business angels like?
In general, business angels, do not like to invest in startups with high operating leverage because it means that the company has high fixed costs and its profitability is highly dependent on sales volume. This increases the risk for investors, as a decline in sales could significantly affect the company's profitability and ultimately its ability to repay its debts. Investors tend to prefer companies with low fixed costs and a more flexible cost structure that allows them to adjust quickly to market conditions.
Business angels generally do not like to invest in startups with a lot of financial leverage because of the high level of risk this represents. Financial leverage increases the company's debt and thus its financial cost, which can negatively affect the company's profitability. Moreover, if the company is unable to repay its debt, this can lead to bankruptcy and the total loss of the investors' investment. Therefore, investors tend to prefer companies with a healthy financial structure and a reasonable level of debt that allows them to grow and expand without high financial risk.
What level of leverage is right for me at each stage of a new venture?
In general, during the early stages of enterprise development, low or no leverage is recommended to reduce financial risk and increase operational flexibility. As the company grows and establishes itself in the market, a moderate level of leverage may be required to finance expansion and growth. However, it is important to balance the level of leverage with the company's ability to generate sufficient cash flow to cover its financial obligations. If the company foresees a large and secure growth in sales, a high level of leverage will be appropriate to increase its profits. While it is true that higher leverage can increase a company's profits, it also implies higher risk. In the case of a company that anticipates large and secure sales growth, a higher level of leverage might be appropriate, allowing it to take advantage of the expected growth without assuming excessive risk in case sales do not develop as expected.
APPLY THIS TIP TO YOUR PROJECT
QUIZZES
- 💻 PRACTICE with an expert in the next practical webinar.
- 🔎 CONSULT more related TIPs with this same theme.
- 📖 AMPLIA your knowledge by downloading this EBOOK y this EBOOK.
THINK ABOUT YOU
- 🚀 IMPULSA your company in the next acceleration programme, ¡book your place now!
- 🥁 PRACTICE with your project in this practical webinar, ¡apply for your place!
- 🌐 CONTACT with other entrepreneurs and companies, ¡register and take part in the next Networking!
THINK ABOUT HELPING OTHERS
- 🤝COLLABORATE as a volunteer: expert, mentor, inverter, awarding, Spreading the word, challenging, innovating, creating a TIP...
- 💬 RECOMMENDS this programme to reach out to more entrepreneurs by Google.
- 👉 SHARE your learning!
- 📲 SEND this TIP 👇









[...] Bargaining leverage, particularly in industries with high fixed costs [...].