VERTICAL INTEGRATION
Accelerate your business with these expert tips on "Vertical Integration". Analyse and discover this TIP!
Vertical integration is a business strategy in which a company takes control of more than one process in the production or distribution chain of its products or services. This strategy is divided into two types: forward integration and backward integration. Vertical forward integration implies that the company acquires control over the distribution and sales processes of its products or services. For example, if a shoe manufacturing company acquires a chain of shoe shops, it would be using forward vertical integration.
On the other hand, backward vertical integration implies that the company takes control of production processes, i.e. it acquires control of suppliers or manufacturers of materials or inputs necessary for its production. For example, if a food production company acquires a farm to produce the food it uses in its production process, it would be using backward vertical integration.
Both types of vertical integration can have advantages for the company, such as controlling costs, improving efficiency and quality of products or services, and reducing lead times and transport costs. However, There may also be disadvantages, such as dependence on internal suppliers or customers and possible loss of flexibility.
Advice to an entrepreneur on how to determine the degree of vertical integration
Here are some tips for an entrepreneur wishing to determine the most appropriate degree of vertical integration for his or her new venture:
- Assessing the industry: Understanding the competitive landscape and industry trends can help determine whether vertical integration is right for the company. If the industry is highly fragmented, vertical integration can offer competitive advantages.
- Assessing the supply chain: assessing the company's supply chain is important in determining whether vertical integration is appropriate. If suppliers or distribution channels are highly competitive and fragmented, it may make sense for the company to vertically integrate to improve efficiency.
- Identify costs: vertical integration may require significant investment in infrastructure, personnel and technology. It is therefore important to assess the potential costs and benefits of vertical integration before making a decision.
- Assess internal resources: the company's ability to manage and operate a vertically integrated supply chain must also be carefully assessed. It is important to determine whether the company has the resources and expertise to manage vertical integration effectively.
- Consider flexibility: vertical integration can limit the flexibility of the company, which can be problematic in a changing business environment. It is therefore important to consider the flexibility of the company and its ability to adapt to changes in the industry.
- Assessing cost-effectiveness: vertical integration should be seen as a long-term investment rather than a short-term solution. It is therefore important to assess the potential for long-term profitability before making a decision.
- Consult experts: Finally, it is recommended that entrepreneurs seek the advice of industry experts or consultants to help them assess the feasibility of vertical integration and determine the appropriate degree of vertical integration for their new venture.
In summary, before deciding whether vertical integration is right for your new venture, it is important to assess the industry, supply chain, costs, internal resources, flexibility and profitability, and to seek expert advice.
Disadvantages of vertical integration for a new company
Additional costs: vertical integration may increase production costs, as the company will have to invest in additional infrastructure, equipment and resources to carry out tasks that were previously carried out by the company. subcontracted (+).
- Lack of flexibility: vertical integration can limit the company's ability to adapt to market changes, as it becomes more difficult to change production or processes when they are controlled internally.
- Risk of obsolescence: investment in technology and equipment necessary for vertical integration may result in obsolete or under-utilised assets in the future.
- Additional responsibility: vertical integration can increase the company's responsibility in areas that were previously handled by third parties, such as safety and regulations.
- Potential conflicts of interest: vertical integration can create potential conflicts of interest, as the company may favour its own internal operations rather than seeking the best interests of its customers or suppliers.
The reasons for vertical integration can be summarised as follows:
- Greater economies of scope. Derived from a better use of resources that can be shared.
- Reduction of intermediate processes. For example, logistics.
- Reduction of transaction costs.
- Achievement of higher margins and thus better profitability of the business.
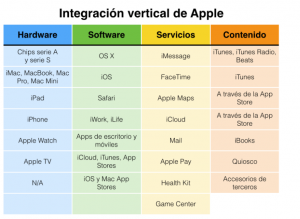
A particularly prominent case of vertical integration is that exercised by Apple, which is responsible for a large part (almost all) of the steps involved in offering its products. It designs, produces the electronic components, assembles them in its factories, promotes them through its communication channels and distributes them in its own shops. There are many examples in the economy where vertical integration is a successful tool for companies, such as the oil companies that extract, process, distribute and market gas oils.
APPLY THIS TIP TO YOUR PROJECT
QUIZ
- 💻 PRACTICE with an expert in the next practical webinar.
- 🔎 CONSULT more related TIPs with this same theme.
- 📖 AMPLIA your knowledge by downloading this EBOOK.
THINK ABOUT YOU
- 🚀 IMPULSA your company in the next acceleration programme, ¡book your place now!
- 🥁 PRACTICE with your project in this practical webinar, ¡apply for your place!.
- 🌐 CONTACT with other entrepreneurs and companies, ¡register and take part in the next Networking!
THINK ABOUT HELPING OTHERS
- 🤝COLLABORATE as a volunteer: expert, mentor, inverter, awarding, Spreading the word, challenging, innovating, creating a TIP...
- 💬 RECOMMENDS this programme to reach out to more entrepreneurs by Google.
- 👉 SHARE your learning!
- 📲 SEND this TIP 👇
Rate this TIP!
Click on the stars to rate
Rating "2" - Average " - Average5"
No votes yet, be the first to vote!
We are sorry you did not find it useful.
Help us improve this TIP!
Leave us a comment and tell us how you would improve this TIP










